Page 45 - Read Online
P. 45
Loong et al. J Transl Genet Genom 2023;7:27-49 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/jtgg.2022.20 Page 39
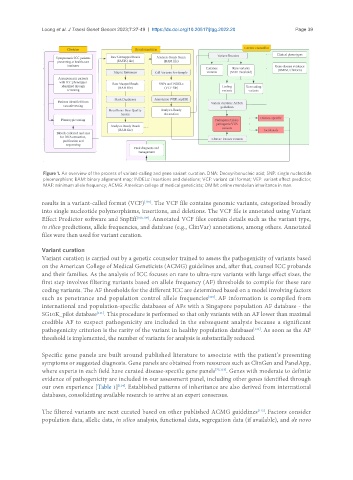
Figure 1. An overview of the process of variant-calling and gene variant curation. DNA: Deoxyribonucleic acid; SNP: single nucleotide
pleomorphism; BAM: binary alignment map; INDELs: insertions and deletions; VCF: variant call format; VEP: variant effect predictor;
MAF: minimum allele frequency; ACMG: American college of medical geneticists; OMIM: online mendelian inheritance in man.
results in a variant-called format (VCF) . The VCF file contains genomic variants, categorized broadly
[107]
into single nucleotide polymorphisms, insertions, and deletions. The VCF file is annotated using Variant
Effect Predictor software and SnpEff [108,109] . Annotated VCF files contain details such as the variant type,
in silico predictions, allele frequencies, and database (e.g., ClinVar) annotations, among others. Annotated
files were then used for variant curation.
Variant curation
Variant curation is carried out by a genetic counselor trained to assess the pathogenicity of variants based
on the American College of Medical Geneticists (ACMG) guidelines and, after that, counsel ICC probands
and their families. As the analysis of ICC focuses on rare to ultra-rare variants with large effect sizes, the
first step involves filtering variants based on allele frequency (AF) thresholds to compile for these rare
coding variants. The AF thresholds for the different ICC are determined based on a model involving factors
such as penetrance and population control allele frequencies . AF information is compiled from
[110]
international and population-specific databases of AFs with a Singapore population AF database - the
SG10K_pilot database . This procedure is performed so that only variants with an AF lower than maximal
[111]
credible AF to suspect pathogenicity are included in the subsequent analysis because a significant
pathogenicity criterion is the rarity of the variant in healthy population databases . As soon as the AF
[112]
threshold is implemented, the number of variants for analysis is substantially reduced.
Specific gene panels are built around published literature to associate with the patient’s presenting
symptoms or suggested diagnosis. Gene panels are obtained from resources such as ClinGen and PanelApp,
where experts in each field have curated disease-specific gene panels [75,113] . Genes with moderate to definite
evidence of pathogenicity are included in our assessment panel, including other genes identified through
[114]
our own experience [Table 1] . Established patterns of inheritance are also derived from international
databases, consolidating available research to arrive at an expert consensus.
[112]
The filtered variants are next curated based on other published ACMG guidelines . Factors consider
population data, allelic data, in silico analysis, functional data, segregation data (if available), and de novo