Page 132 - Read Online
P. 132
Page 126 Chan et al. J Transl Genet Genom 2024;8:13-34 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/jtgg.2023.36
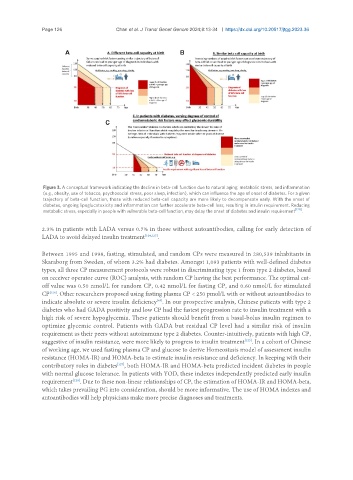
Figure 3. A conceptual framework indicating the decline in beta-cell function due to natural aging, metabolic stress, and inflammation
(e.g., obesity, use of tobacco, psychosocial stress, poor sleep, infection), which can influence the age of onset of diabetes. For a given
trajectory of beta-cell function, those with reduced beta-cell capacity are more likely to decompensate early. With the onset of
diabetes, ongoing lipoglucotoxicity and inflammation can further accelerate beta-cell loss, resulting in insulin requirement. Reducing
metabolic stress, especially in people with vulnerable beta-cell function, may delay the onset of diabetes and insulin requirement [128] .
2.3% in patients with LADA versus 0.7% in those without autoantibodies, calling for early detection of
LADA to avoid delayed insulin treatment [124,125] .
Between 1995 and 1998, fasting, stimulated, and random CPs were measured in 280,539 inhabitants in
Skaraborg from Sweden, of whom 3.2% had diabetes. Amongst 1,093 patients with well-defined diabetes
types, all three CP measurement protocols were robust in discriminating type 1 from type 2 diabetes, based
on receiver operator curve (ROC) analysis, with random CP having the best performance. The optimal cut-
off value was 0.50 nmol/L for random CP, 0.42 nmol/L for fasting CP, and 0.60 nmol/L for stimulated
[126]
CP . Other researchers proposed using fasting plasma CP < 250 pmol/L with or without autoantibodies to
indicate absolute or severe insulin deficiency . In our prospective analysis, Chinese patients with type 2
[46]
diabetes who had GADA positivity and low CP had the fastest progression rate to insulin treatment with a
high risk of severe hypoglycemia. These patients should benefit from a basal-bolus insulin regimen to
optimize glycemic control. Patients with GADA but residual CP level had a similar risk of insulin
requirement as their peers without autoimmune type 2 diabetes. Counter-intuitively, patients with high CP,
[125]
suggestive of insulin resistance, were more likely to progress to insulin treatment . In a cohort of Chinese
of working age, we used fasting plasma CP and glucose to derive Homeostasis model of assessment insulin
resistance (HOMA-IR) and HOMA-beta to estimate insulin resistance and deficiency. In keeping with their
contributory roles in diabetes , both HOMA-IR and HOMA-beta predicted incident diabetes in people
[127]
with normal glucose tolerance. In patients with YOD, these indexes independently predicted early insulin
requirement . Due to these non-linear relationships of CP, the estimation of HOMA-IR and HOMA-beta,
[128]
which takes prevailing PG into consideration, should be more informative. The use of HOMA indexes and
autoantibodies will help physicians make more precise diagnoses and treatments.