Page 492 - Read Online
P. 492
Huang et al. J Cancer Metastasis Treat 2019;5:34 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-4722.2018.94 Page 3 of 18
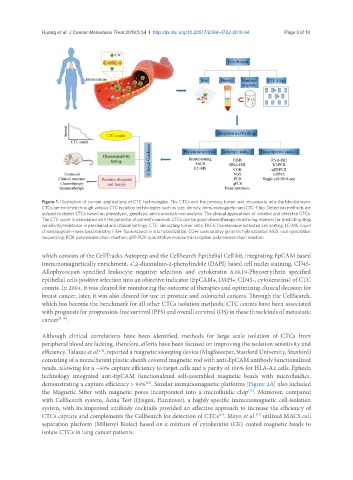
Figure 1. Illustration of current applications of CTC technologies. The CTCs exit the primary tumor and intravasate into the bloodstream.
CTCs are enriched through various CTC isolation technologies such as size, density, immunomagnetic and CTC-Chip. Detection methods are
utilized to detect CTCs based on phenotypic, genotypic and transcriptional analysis. The clinical applications of isolated and detected CTCs.
The CTC count is associated with the potential of patient’s survival. CTCs can be good chemotherapy monitoring markers for predicting drug
sensitivity/resistance in preclinical and clinical settings. CTC: circulating tumor cells; FACS: fluorescence activated cell sorting; LC-MS: liquid
chromatograph-mass spectrometry; FISH: fluorescence in situ hybridization; CGH: comparative genomic hybridization; NGS: next-generation
sequencing; PCR: polymerase chain reaction; qRT-PCR: quantitative reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction
which consists of the CellTracks Autoprep and the CellSearch Epithelial Cell kit, integrating EpCAM based
immunomagnetically enrichment, 4’,2-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI) based cell nuclei staining, CD45-
Allophycocyan specified leukocyte negative selection and cytokeratin 8,18,19-Phycoerythrin specified
epithelial cells positive selection into an objective indicator (EpCAM+, DAPI+, CD45-, cytokeratin+) of CTC
counts. In 2004, it was cleared for monitoring the outcome of therapies and optimizing clinical decision for
breast cancer; later, it was also cleared for use in prostate and colorectal cancers. Through the CellSearch,
which has become the benchmark for all other CTCs isolation methods, CTC counts have been associated
with prognosis for progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) in these three kinds of metastatic
cancer [8-10] .
Although clinical correlations have been identified, methods for large scale isolation of CTCs from
peripheral blood are lacking, therefore, efforts have been focused on improving the isolation sensitivity and
efficiency. Talasaz et al. , reported a magnetic sweeping device (MagSweeper, Stanford University, Stanford)
[11]
consisting of a nonadherent plastic sheath covered magnetic rod with anti-EpCAM antibody functionalized
beads, allowing for a ~60% capture efficiency to target cells and a purity of 100% for HLA-A2 cells. Ephesia
technology integrated anti-EpCAM functionalized self-assembled magnetic beads with microfluidics,
demonstrating a capture efficiency > 94% . Similar immunomagnetic platforms [Figure 2A] also included
[12]
the Magnetic Sifter with magnetic pores incorporated into a microfluidic chip . Moreover, compared
[13]
with CellSearch system, Adna Test (Qiagen, Hannover), a highly specific immunomagnetic cell-isolation
system, with its improved antibody cocktails provided an effective approach to increase the efficiency of
CTCs capture and complements the CellSearch for detection of CTCs . Mayo et al. utilized MACS cell
[15]
[14]
separation platform (Miltenyi Biotec) based on a mixture of cytokeratin (CK) coated magnetic beads to
isolate CTCs in lung cancer patients.