Page 316 - Read Online
P. 316
Page 2 of 23 Monks et al. J Cancer Metastasis Treat 2019;5:24 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-4722.2018.79
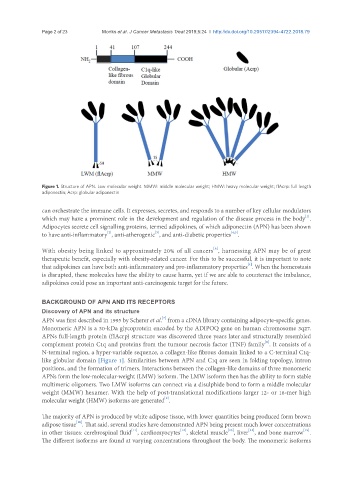
Figure 1. Structure of APN. Low molecular weight. MMW: middle molecular weight; HMW: heavy molecular weight; flAcrp: full length
adiponectin; Acrp: globular adiponectin
can orchestrate the immune cells. It expresses, secretes, and responds to a number of key cellular modulators
[1]
which may have a prominent role in the development and regulation of the disease process in the body .
Adipocytes secrete cell signalling proteins, termed adipokines, of which adiponectin (APN) has been shown
[4,5]
[3]
to have anti-inflammatory , anti-atherogenic , and anti-diabetic properties .
[2]
[6]
With obesity being linked to approximately 20% of all cancers , harnessing APN may be of great
therapeutic benefit, especially with obesity-related cancer. For this to be successful, it is important to note
[4]
that adipokines can have both anti-inflammatory and pro-inflammatory properties . When the homeostasis
is disrupted, these molecules have the ability to cause harm, yet if we are able to counteract the imbalance,
adipokines could pose an important anti-carcinogenic target for the future.
BACKGROUND OF APN AND ITS RECEPTORS
Discovery of APN and its structure
APN was first described in 1995 by Scherer et al. from a cDNA library containing adipocyte-specific genes.
[7]
Monomeric APN is a 30-kDa glycoprotein encoded by the ADIPOQ gene on human chromosome 3q27.
APNs full-length protein (flAcrp) structure was discovered three years later and structurally resembled
[8]
complement protein C1q and proteins from the tumour necrosis factor (TNF) family . It consists of a
N-terminal region, a hyper-variable sequence, a collagen-like fibrous domain linked to a C-terminal C1q-
like globular domain [Figure 1]. Similarities between APN and C1q are seen in folding topology, intron
positions, and the formation of trimers. Interactions between the collagen-like domains of three monomeric
APNs form the low-molecular-weight (LMW) isoform. The LMW isoform then has the ability to form stable
multimeric oligomers. Two LMW isoforms can connect via a disulphide bond to form a middle molecular
weight (MMW) hexamer. With the help of post-translational modifications larger 12- or 18-mer high
molecular weight (HMW) isoforms are generated .
[9]
The majority of APN is produced by white adipose tissue, with lower quantities being produced form brown
[10]
adipose tissue . That said, several studies have demonstrated APN being present much lower concentrations
[15]
[14]
[12]
[11]
[13]
in other tissues: cerebrospinal fluid , cardiomyocytes , skeletal muscle , liver , and bone marrow .
The different isoforms are found at varying concentrations throughout the body. The monomeric isoforms