Page 276 - Read Online
P. 276
Ansari et al. J Cancer Metastasis Treat 2019;5:20 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-4722.2018.68 Page 11 of 14
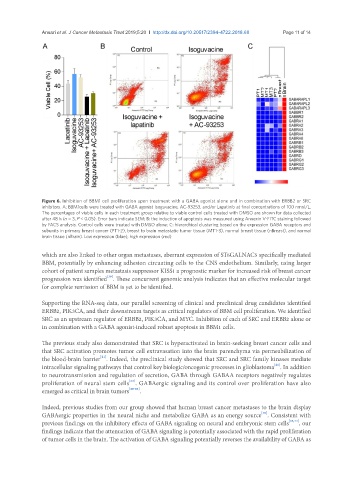
Figure 6. Inhibition of BBM1 cell proliferation upon treatment with a GABA agonist alone and in combination with ERBB2 or SRC
inhibitors. A: BBM1cells were treated with GABA agonist Isoguvacine, AC-93253, and/or Lapatinib at final concentrations of 100 nmol/L.
The percentages of viable cells in each treatment group relative to viable control cells treated with DMSO are shown for data collected
after 48 h (n = 3, P < 0.05). Error bars indicate SEM; B: the induction of apoptosis was measured using Annexin V-FITC staining followed
by FACS analysis. Control cells were treated with DMSO alone; C: hierarchical clustering based on the expression GABA receptors and
subunits in primary breast cancer (PT1-2), breast to brain metastatic tumor tissue (MT1-3), normal breast tissue (nBreast), and normal
brain tissue (nBrain). Low expression (blue), high expression (red)
which are also linked to other organ metastases, aberrant expression of ST6GALNAC5 specifically mediated
BBM, potentially by enhancing adhesion circuating cells to the CNS endothelium. Similarly, using larger
cohort of patient samples metastasis suppressor KISS1 a prognostic marker for increased risk of breast cancer
[39]
progression was identified . These concurrent genomic analysis indicates that an effective molecular target
for complete remission of BBM is yet to be identified.
Supporting the RNA-seq data, our parallel screening of clinical and preclinical drug candidates identified
ERBB2, PIK3CA, and their downstream targets as critical regulators of BBM cell proliferation. We identified
SRC as an upstream regulator of ERBB2, PIK3CA, and MYC. Inhibition of each of SRC and ERBB2 alone or
in combination with a GABA agonist-induced robust apoptosis in BBM1 cells.
The previous study also demonstrated that SRC is hyperactivated in brain-seeking breast cancer cells and
that SRC activation promotes tumor cell extravasation into the brain parenchyma via permeabilization of
[21]
the blood-brain barrier . Indeed, the preclinical study showed that SRC and SRC family kinases mediate
[21]
intracellular signaling pathways that control key biologic/oncogenic processes in glioblastoma . In addition
to neurotransmission and regulation of secretion, GABA through GABAA receptors negatively regulates
[23]
proliferation of neural stem cells . GABAergic signaling and its control over proliferation have also
emerged as critical in brain tumors [40-42] .
Indeed, previous studies from our group showed that human breast cancer metastases to the brain display
[40]
GABAergic properties in the neural niche and metabolize GABA as an energy source . Consistent with
previous findings on the inhibitory effects of GABA signaling on neural and embryonic stem cells [43,44] , our
findings indicate that the attenuation of GABA signaling is potentially associated with the rapid proliferation
of tumor cells in the brain. The activation of GABA signaling potentially reverses the availability of GABA as