Page 363 - Read Online
P. 363
Pereira et al. J Cancer Metastasis Treat 2018;4:30 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-4722.2018.13 Page 3 of 14
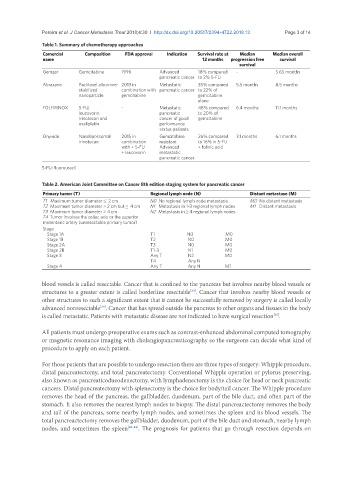
Table 1. Summary of chemotherapy approaches
Comercial Composition FDA approval Indication Survival rate at Median Median overall
name 12 months progression free survival
survival
Gemzar Gemcitabine 1996 Advanced 18% compared - 5.65 months
pancreatic cancer to 2% 5-FU
Abraxane Paclitaxel albumine- 2013 in Metastatic 35% compared 5.5 months 8.5 months
stabilized combination with pancreatic cancer to 22% of
nanoparticle gemcitabine gemcitabine
alone
FOLFIRINOX 5-FU, - Metastatic 48% compared 6.4 months 11.1 months
leucovorin, pancreatic to 20% of
Irinotecan and cancer of good gemcitabine
oxaliplatin performance
status patients
Onyvide Nanolipossomal 2015 in Gemcitabine 26% compared 3.1 months 6.1 months
irinotecan combination resistant to 16% in 5-FU
with + 5-FU Advanced + folinic acid
+ leucovorin metastatic
pancreatic cancer
5-FU: fluorouracil
Table 2. American Joint Committee on Cancer 8th edition staging system for pancreatic cancer
Primary tumor (T) Regional lymph node (N) Distant metastase (M)
T1 Maximum tumor diameter ≤ 2 cm N0 No regional lymph node metastasis M0 No distant metastasis
T2 Maximum tumor diameter > 2 cm but ≤ 4 cm N1 Metastasis in 1-3 regional lymph nodes M1 Distant metastasis
T3 Maximum tumor diameter > 4 cm N2 Metastasis in ≥ 4 regional lymph nodes
T4 Tumor involves the celiac axis or the superior
mesenteric artery (unresectable primary tumor)
Stage
Stage 1A T1 N0 M0
Stage 1B T2 N0 M0
Stage 2A T3 N0 M0
Stage 2B T1-3 N1 M0
Stage 3 Any T N2 M0
T4 Any N
Stage 4 Any T Any N M1
blood vessels is called resectable. Cancer that is confined to the pancreas but involves nearby blood vessels or
structures to a greater extent is called borderline resectable . Cancer that involves nearby blood vessels or
[23]
other structures to such a significant extent that it cannot be successfully removed by surgery is called locally
advanced nonresectable . Cancer that has spread outside the pancreas to other organs and tissues in the body
[24]
is called metastatic. Patients with metastatic disease are not indicated to have surgical resection .
[25]
All patients must undergo preoperative exams such as contrast-enhanced abdominal computed tomography
or magnetic resonance imaging with cholangiopancreaticography so the surgeons can decide what kind of
procedure to apply on each patient.
For those patients that are possible to undergo resection there are three types of surgery: Whipple procedure,
distal pancreatectomy, and total pancreatectomy. Conventional Whipple operation or pylorus preserving,
also known as pancreaticodueodenectomy, with lymphadenectomy is the choice for head or neck pancreatic
cancers. Distal pancreatectomy with splenectomy is the choice for body/tail cancer. The Whipple procedure
removes the head of the pancreas, the gallbladder, duodenum, part of the bile duct, and often part of the
stomach. It also removes the nearest lymph nodes to biopsy. The distal pancreactectomy removes the body
and tail of the pancreas, some nearby lymph nodes, and sometimes the spleen and its blood vessels. The
total pancreactectomy removes the gallbladder, duodenum, part of the bile duct and stomach, nearby lymph
nodes, and sometimes the spleen [26-28] . The prognosis for patients that go through resection depends on