Page 253 - Read Online
P. 253
Parsons et al. J Cancer Metastasis Treat 2018;4:19 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-4722.2018.11 Page 7 of 23
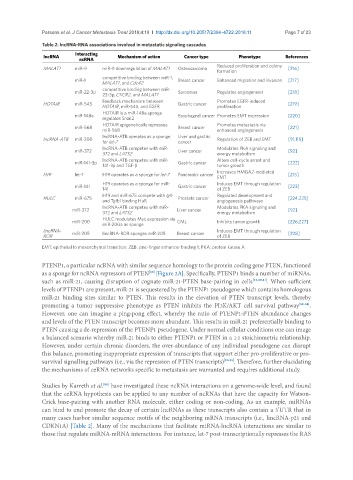
Table 2. lncRNA-RNA associations involved in metastatic signaling cascades
lncRNA Interacting Mechanism of action Cancer type Phenotype References
ncRNA
Reduced proliferation and colony
MALAT1 miR-9 miR-9 downregulation of MALAT1 Osteosarcoma [216]
formation
competitive binding between miR-1,
miR-1 Breast cancer Enhanced migration and invasion [217]
MALAT1, and Cdc42
competitive binding between miR-
miR-22-3p Sarcomas Regulates angiogenesis [218]
22-3p, CXCR2, and MALAT1
Feedback mechanism between Promotes EGFR-induced
HOTAIR miR-545 Gastric cancer [219]
HOTAIR, miR-545, and EGFR proliferation
HOTAIR is a miR-148a sponge
miR-148a Esophageal cancer Promotes EMT expression [220]
regulates Snail2
HOTAIR epigenetically represses Promotes metastasis via
miR-568 Breast cancer [221]
miR-568 enhanced angiogenesis
lncRNA-ATB operates as a sponge Liver and gastric
lncRNA-ATB miR-200 Regulation of ZEB and EMT [91,115]
for let-7 cancer
lncRNA-ATB competes with miR- Modulates PKA signaling and
miR-372 Liver cancer [92]
372 and LATS2 energy metabolism
lncRNA-ATB competes with miR- Alters cell-cycle arrest and
miR-141-3p 141-3p and TGF-β Gastric cancer tumor growth [222]
Increases HMGA2-mediated
H19 let-7 H19 operates as a sponge for let-7 Pancreatic cancer [215]
EMT
H19 operates as a sponge for miR- Induces EMT through regulation
miR-141 Gastric cancer [223]
141 of ZEB
H19 and miR-675 compete with Igfr Regulated development and
HULC miR-675 Prostate cancer [224,225]
and Tgfb1 binding HuR angiogenesis pathways
lncRNA-ATB competes with miR- Modulates PKA signaling and
miR-372 Liver cancer [92]
372 and LATS2 energy metabolism
HULC modulates Myc expression via
miR-200 CML Inhibits tumor growth [226,227]
miR-200a as sponge
lincRNA- miR-205 lincRNA-ROR sponges miR-205 Breast cancer Induces EMT through regulation [228]
ROR of ZEB
EMT: epithelial to mesenchymal transition; ZEB: zinc-finger enhancer binding 1; PKA: protein kinase A
PTENP1, a particular ncRNA with similar sequence homology to the protein coding gene PTEN, functioned
as a sponge for ncRNA repressors of PTEN [Figure 2A]. Specifically, PTENP1 binds a number of miRNAs,
[80]
such as miR-21, causing disruption of cognate miR-21-PTEN base-pairing in cells [24,80,81] . When sufficient
levels of PTENP1 are present, miR-21 is sequestered by the PTENP1 pseudogene which contains homologous
miR-21 binding sites similar to PTEN. This results in the elevation of PTEN transcript levels, thereby
promoting a tumor suppressive phenotype as PTEN inhibits the PI3K/AKT cell survival pathway [82-84] .
However, one can imagine a ping-pong effect, whereby the ratio of PTENP1-PTEN abundance changes
and levels of the PTEN transcript becomes more abundant. This results in miR-21 preferentially binding to
PTEN causing a de-repression of the PTENP1 pseudogene. Under normal cellular conditions one can image
a balanced scenario whereby miR-21 binds to either PTENP1 or PTEN in a 1:1 stoichiometric relationship.
However, under certain chronic disorders, the over-abundance of any individual pseudogene can disrupt
this balance, promoting inappropriate expression of transcripts that support either pro-proliferative or pro-
survival signalling pathways (i.e., via the repression of PTEN transcripts) [80,85] . Therefore, further elucidating
the mechanisms of ceRNA networks specific to metastasis are warranted and requires additional study.
Studies by Karreth et al. have investigated these ncRNA interactions on a genome-wide level, and found
[86]
that the ceRNA hypothesis can be applied to any number of ncRNAs that have the capacity for Watson-
Crick base-pairing with another RNA molecule, either coding or non-coding. As an example, miRNAs
can bind to and promote the decay of certain lncRNAs as these transcripts also contain a 3’UTR that in
many cases harbor similar sequence motifs of the neighboring mRNA transcripts (i.e., lincRNA-p21 and
CDKN1A) [Table 2]. Many of the mechanisms that facilitate miRNA-lncRNA interactions are similar to
those that regulate miRNA-mRNA interactions. For instance, let-7 post-transcriptionally represses the RAS