Page 252 - Read Online
P. 252
Page 6 of 23 Parsons et al. J Cancer Metastasis Treat 2018;4:19 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-4722.2018.11
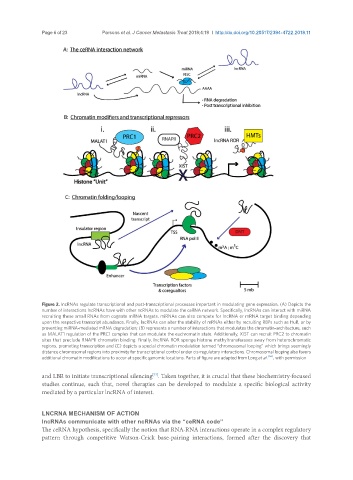
Figure 2. lncRNAs regulate transcriptional and post-transcriptional processes important in modulating gene expression. (A) Depicts the
number of interactions lncRNAs have with other ncRNAs to modulate the ceRNA network. Specifically, lncRNAs can interact with miRNA
recruiting these small RNAs from cognate mRNA targets. miRNAs can also compete for lncRNA or mRNA target binding depending
upon the respective transcript abundance. Finally, lncRNAs can alter the stability of mRNAs either by recruiting RBPs such as HuR, or by
preventing miRNA-mediated mRNA degradation; (B) represents a number of interactions that modulates the chromatin-architecture, such
as MALAT1 regulation of the PRC1 complex that can modulate the euchromatin state. Additionally, XIST can recruit PRC2 to chromatin
sites that preclude RNAPII chromatin binding. Finally, lncRNA ROR sponge histone methyltransferases away from heterochromatic
regions, promoting transcription and (C) depicts a special chromatin modulation termed “chromosomal looping” which brings seemingly
distance chromosomal regions into proximity for transcriptional control under cis-regulatory interactions. Chromosomal looping also favors
additional chromatin modifications to occur at specific genomic locations. Parts of figure are adapted from Long et al. [66] , with permission
and LBR to initiate transcriptional silencing . Taken together, it is crucial that these biochemistry-focused
[77]
studies continue, such that, novel therapies can be developed to modulate a specific biological activity
mediated by a particular lncRNA of interest.
LNCRNA MECHANISM OF ACTION
lncRNAs communicate with other ncRNAs via the “ceRNA code”
The ceRNA hypothesis, specifically the notion that RNA-RNA interactions operate in a complex regulatory
pattern through competitive Watson-Crick base-pairing interactions, formed after the discovery that