Page 117 - Read Online
P. 117
Page 4 of 6 Macedo et al. J Cancer Metastasis Treat 2018;4:8 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-4722.2017.72
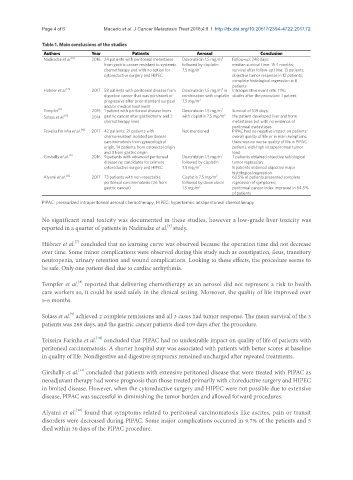
Table 1. Main conclusions of the studies
Authors Year Patients Aerosol Conclusion
Nadiradze et al. [6] 2016 24 patients with peritoneal metastases Doxorubicin 1.5 mg/m 2 Follow-up: 248 days;
from gastric cancer resistant to systemic followed by cisplatin median survival time: 15.4 months;
chemotherapy and with no option for 7.5 mg/m 2 survival after follow-up time: 13 patients;
cytoreductive surgery and HIPEC objective tumor response in 12 patients;
complete histological regression in 6
patients
2
Hübner et al. [7] 2017 58 patients with peritoneal disease from Doxorubicin 1.5 mg/m in Intraoperative event rate: 11%;
digestive cancer that was persistent or combination with cisplatin deaths after the procedure: 1 patient
progressive after prior standard surgical 7.5 mg/m 2
and/or medical treatment
Tempfer [8] 2015 1 patient with peritoneal disease from Doxorubicin 1.5 mg/m 2 Survival of 109 days;
Solass et al. [9] 2014 gastric cancer after gastrectomy and 2 with cisplatin 7.5 mg/m 2 the patient developed liver and bone
chemotherapy lines metastases but with no evidence of
peritoneal metastases
Teixeira Farinha et al. [10] 2017 42 patients: 21 patients with Not mentioned PIPAC had no negative impact on patients’
chemoresistent isolated peritoneal overall quality of life or in main symptoms;
carcinomatosis from gynecological there was no worse quality of life in PIPAC
origin, 14 patients from colorectal origin patients with high intraperitoneal tumor
and 3 from gastric origin load
Girshally et al. [11] 2016 9 patients with advanced peritoneal Doxorubicin 1.5 mg/m 2 7 patients obtained objective radiological
disease no candidates for primary followed by cisplatin tumor regression;
cytoreductive surgery and HIPEC 7.5 mg/m 2 8 patients obtained objective major
histological regression
Alyami et al. [12] 2017 73 patients with non-resectable Cisplatin 7.5 mg/m 2 63.5% of patients presented complete
peritoneal carcinomatosis (26 from followed by doxorubicin regression of symptoms;
gastric cancer) 1.5 mg/m 2 peritoneal cancer index improved in 64.5%
of patients
PIPAC: pressurized intraperitoneal aerosol chemotherapy; HIPEC: hypertermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy
No significant renal toxicity was documented in these studies, however a low-grade liver toxicity was
[6]
reported in a quarter of patients in Nadiradze et al. study.
[7]
Hübner et al. concluded that no learning curve was observed because the operation time did not decrease
over time. Some minor complications were observed during this study such as constipation, ileus, transitory
neutropenia, urinary retention and wound complications. Looking to these effects, the procedure seems to
be safe. Only one patient died due to cardiac arrhythmia.
[8]
Tempfer et al. reported that delivering chemotherapy as an aerosol did not represent a risk to health
care workers so, it could be used safely in the clinical setting. Moreover, the quality of life improved over
5-6 months.
[9]
Solass et al. achieved 2 complete remissions and all 3 cases had tumor response. The mean survival of the 3
patients was 288 days, and the gastric cancer patients died 109 days after the procedure.
[10]
Teixeira Farinha et al. concluded that PIPAC had no undesirable impact on quality of life of patients with
peritoneal carcinomatosis. A shorter hospital stay was associated with patients with better scores at baseline
in quality of life. Nondigestive and digestive symptoms remained uncharged after repeated treatments.
[11]
Girshally et al. concluded that patients with extensive peritoneal disease that were treated with PIPAC as
neoadjuvant therapy had worse prognosis than those treated primarily with citoreductive surgery and HIPEC
in limited disease. However, when the cytoreductive surgery and HIPEC were not possible due to extensive
disease, PIPAC was successful in diminishing the tumor burden and allowed forward procedures.
[12]
Alyami et al. found that symptoms related to peritoneal carcinomatosis like ascites, pain or transit
disorders were decreased during PIPAC. Some major complications occurred in 9.7% of the patients and 5
died within 30 days of the PIPAC procedure.