Page 116 - Read Online
P. 116
Macedo et al. J Cancer Metastasis Treat 2018;4:8 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-4722.2017.72 Page 3 of 6
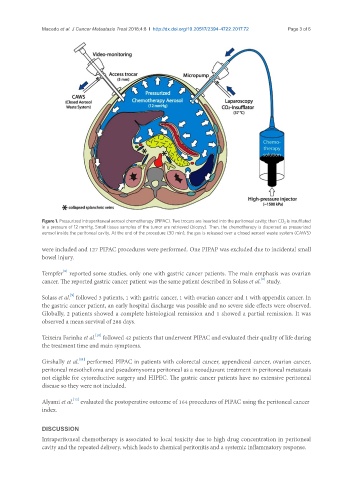
Figure 1. Pressurized intraperitoneal aerosol chemotherapy (PIPAC). Two trocars are inserted into the peritoneal cavity; then CO 2 is insufflated
in a pressure of 12 mmHg. Small tissue samples of the tumor are retrieved (biopsy). Then, the chemotherapy is dispersed as pressurized
aerosol inside the peritoneal cavity. At the end of the procedure (30 min), the gas is released over a closed aerosol waste system (CAWS)
were included and 127 PIPAC procedures were performed. One PIPAP was excluded due to incidental small
bowel injury.
[8]
Tempfer reported some studies, only one with gastric cancer patients. The main emphasis was ovarian
[9]
cancer. The reported gastric cancer patient was the same patient described in Solass et al. study.
[9]
Solass et al. followed 3 patients, 1 with gastric cancer, 1 with ovarian cancer and 1 with appendix cancer. In
the gastric cancer patient, an early hospital discharge was possible and no severe side effects were observed.
Globally, 2 patients showed a complete histological remission and 1 showed a partial remission. It was
observed a mean survival of 288 days.
Teixeira Farinha et al. followed 42 patients that underwent PIPAC and evaluated their quality of life during
[10]
the treatment time and main symptoms.
[11]
Girshally et al. performed PIPAC in patients with colorectal cancer, appendiceal cancer, ovarian cancer,
peritoneal mesothelioma and pseudomyxoma peritoneal as a neoadjuvant treatment in peritoneal metastasis
not eligible for cytoreductive surgery and HIPEC. The gastric cancer patients have no extensive peritoneal
disease so they were not included.
[12]
Alyami et al. evaluated the postoperative outcome of 164 procedures of PIPAC using the peritoneal cancer
index.
DISCUSSION
Intraperitoneal chemotherapy is associated to local toxicity due to high drug concentration in peritoneal
cavity and the repeated delivery, which leads to chemical peritonitis and a systemic inflammatory response.