Page 370 - Read Online
P. 370
Xiong et al. ECM in tumor progression
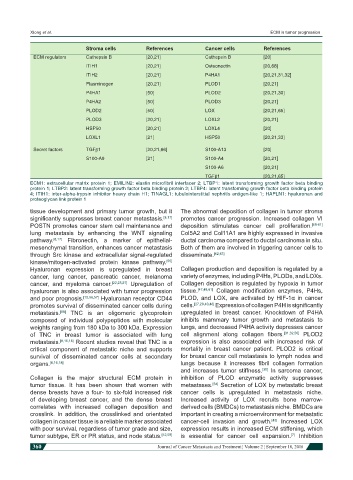
Stroma cells References Cancer cells References
ECM regulators Cathepsin B [20,21] Cathepsin B [20]
ITIH1 [20,21] Osteonectin [20,68]
ITIH2 [20,21] P4HA1 [20,21,31,32]
Plasminogen [20,21] PLOD1 [20,21]
P4HA1 [50] PLOD2 [20,21,30]
P4HA2 [50] PLOD3 [20,21]
PLOD2 [50] LOX [20,21,65]
PLOD3 [20,21] LOXL2 [20,21]
HSP50 [20,21] LOXL4 [20]
LOXL1 [21] HSP50 [20,21,33]
Secret factors TGFβ1 [20,21,66] S100-A13 [20]
S100-A9 [21] S100-A4 [20,21]
S100-A6 [20,21]
TGFβ1 [20,21,65]
ECM1: extracellular matrix protein 1; EMILIN2: elastin microfibril interfacer 2; LTBP1: latent transforming growth factor beta binding
protein 1; LTBP2: latent transforming growth factor beta binding protein 2; LTBP4: latent transforming growth factor beta binding protein
4; ITIH1: inter-alpha-trypsin inhibitor heavy chain H1; TINAGL1: tubulointerstitial nephritis antigen-like 1; HAPLN1: hyaluronan and
proteoglycan link protein 1
tissue development and primary tumor growth, but it The abnormal deposition of collagen in tumor stroma
significantly suppresses breast cancer metastasis. [8,17] promotes cancer progression. Increased collagen VI
POSTN promotes cancer stem cell maintenance and deposition stimulates cancer cell proliferation. [59-61]
lung metastasis by enhancing the WNT signaling Col5A2 and Col11A1 are highly expressed in invasive
pathway. [8,17] Fibronectin, a marker of epithelial- ductal carcinoma compared to ductal carcinoma in situ.
mesenchymal transition, enhances cancer metastasis Both of them are involved in triggering cancer cells to
through Src kinase and extracellular signal-regulated disseminate. [62,63]
kinase/mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway.
[55]
Hyaluronan expression is upregulated in breast Collagen production and deposition is regulated by a
cancer, lung cancer, pancreatic cancer, melanoma variety of enzymes, including P4Hs, PLODs, and LOXs.
cancer, and myeloma cancer. [22,23,27] Upregulation of Collagen deposition is regulated by hypoxia in tumor
hyaluronan is also associated with tumor progression tissue. [47,48,61] Collagen modification enzymes, P4Hs,
and poor prognosis. [15,56,57] Hyaluronan receptor CD44 PLOD, and LOX, are activated by HIF-1α in cancer
promotes survival of disseminated cancer cells during cells. [27,28,40,48] Expression of collagen P4H is significantly
metastasis. TNC is an oligomeric glycoprotein upregulated in breast cancer. Knockdown of P4HA
[58]
composed of individual polypeptides with molecular inhibits mammary tumor growth and metastasis to
weights ranging from 180 kDa to 300 kDa. Expression lungs, and decreased P4HA activity depresses cancer
of TNC in breast tumor is associated with lung cell alignment along collagen fibers. [31,32,50] PLOD2
metastasis. [8,16,18] Recent studies reveal that TNC is a expression is also associated with increased risk of
critical component of metastatic niche and supports mortality in breast cancer patient. PLOD2 is critical
survival of disseminated cancer cells at secondary for breast cancer cell metastasis to lymph nodes and
organs. [8,16,18] lungs because it increases fibril collagen formation
and increases tumor stiffness. In sarcoma cancer,
[30]
Collagen is the major structural ECM protein in inhibition of PLOD enzymatic activity suppresses
tumor tissue. It has been shown that women with metastases. Secretion of LOX by metastatic breast
[64]
dense breasts have a four- to six-fold increased risk cancer cells is upregulated in metastasis niche.
of developing breast cancer, and the dense breast Increased activity of LOX recruits bone marrow-
correlates with increased collagen deposition and derived cells (BMDCs) to metastasis niche. BMDCs are
crosslink. In addition, the crosslinked and orientated important in creating a microenvironment for metastatic
collagen in cancer tissue is a reliable marker associated cancer-cell invasion and growth. Increased LOX
[43]
with poor survival, regardless of tumor grade and size, expression results in increased ECM stiffening, which
tumor subtype, ER or PR status, and node status. [12,59] is essential for cancer cell expansion. Inhibition
[7]
360 Journal of Cancer Metastasis and Treatment ¦ Volume 2 ¦ September 18, 2016