Page 11 - Read Online
P. 11
Page 6 of 12 Schaafsma et al. J Cancer Metastasis Treat 2021;7:34 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-4722.2021.72
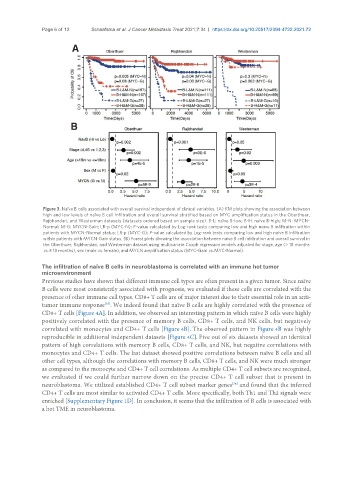
Figure 3. Naïve B cells associated with overall survival independent of clinical variables. (A) KM plots showing the association between
high and low levels of naïve B cell infiltration and overall survival stratified based on MYC amplification status in the Oberthuer,
Rajbhandari, and Westerman datasets (datasets ordered based on sample size). B-L: naïve B-low; B-H: naïve B-high; M-N: MYCN-
Normal; M-G: MYCN-Gain; LR-p (MYC-N): P-value calculated by Log-rank tests comparing low and high naïve B infiltration within
patients with MYCN-Normal status; LR-p (MYC-G): P-value calculated by Log-rank tests comparing low and high naïve B infiltration
within patients with MYCN-Gain status. (B) Forest plots showing the association between naïve B cell infiltration and overall survival in
the Oberthuer, Rajbhandari, and Westerman dataset using multivariate Coxph regression models adjusted for stage, age (> 18 months
vs. ≤ 18 months), sex (male vs. female), and MYCN amplification status (MYC-Gain vs. MYC-Normal).
The infiltration of naïve B cells in neuroblastoma is correlated with an immune hot tumor
microenvironment
Previous studies have shown that different immune cell types are often present in a given tumor. Since naïve
B cells were most consistently associated with prognosis, we evaluated if these cells are correlated with the
presence of other immune cell types. CD8+ T cells are of major interest due to their essential role in an anti-
tumor immune response . We indeed found that naïve B cells are highly correlated with the presence of
[33]
CD8+ T cells [Figure 4A]. In addition, we observed an interesting pattern in which naïve B cells were highly
positively correlated with the presence of memory B cells, CD8+ T cells, and NK cells, but negatively
correlated with monocytes and CD4+ T cells [Figure 4B]. The observed pattern in Figure 4B was highly
reproducible in additional independent datasets [Figure 4C]. Five out of six datasets showed an identical
pattern of high correlations with memory B cells, CD8+ T cells, and NK, but negative correlations with
monocytes and CD4+ T cells. The last dataset showed positive correlations between naïve B cells and all
other cell types, although the correlations with memory B cells, CD8+ T cells, and NK were much stronger
as compared to the monocyte and CD4+ T cell correlations. As multiple CD4+ T cell subsets are recognized,
we evaluated if we could further narrow down on the precise CD4+ T cell subset that is present in
neuroblastoma. We utilized established CD4+ T cell subset marker genes and found that the inferred
[34]
CD4+ T cells are most similar to activated CD4+ T cells. More specifically, both Th1 and Th2 signals were
enriched [Supplementary Figure 1D]. In conclusion, it seems that the infiltration of B cells is associated with
a hot TME in neuroblastoma.