Page 64 - Read Online
P. 64
[Table 1]. In esophageal cancer, RT-PCR was the main Gastric cancer
technique to detect CTCs in previous studies. [42-45] As for
available molecular markers, CEA and SCC are useful A number of studies of CTC detection in patients
predictive markers for tumor recurrence and survival. with gastric cancer have been reported previously
Most recently, a large-scale of study using CellSearch as summarized in Table 2. Although the several
System , morphological technique are also reported. [46,47] methodology of CTC detection including RT-PCR
®
®
Matsushita et al. revealed that CTC detection by and CellSearch System [Table 2], it remains unclear
[46]
CellSearch System was useful to evaluate the clinical which is the best method and molecular marker for
®
effi cacy of chemotherapy and chemoradiation therapy detection of CTCs in gastric cancer patients. Recently,
on esophageal cancer patients. Reeh et al. reported various meta-analyses demonstrated that presence of
[47]
that patients with positive CTCs had signifi cantly poorer CTCs was associated with poor prognosis and advanced
overall survival and progression-free survival rate; clinicopathological factors. [48-50] It has been reported that
therefore, preoperative CTC detection by CellSearch detection of CTCs in gastric cancer may be useful in
System was an independent prognostic indicator for early diagnosis and monitoring of treatment responses
®
patients with esophageal cancer. However, most of and prognosis. However, as for diagnosis, a recent
previously reported patients had esophageal squamous meta-analysis showed that CTC detection alone cannot
cell carcinoma. There are some differences of biological be recommended as a screening test for gastric cancer
behaviors between esophageal squamous cell carcinoma because of lower and inconsistent sensitivity estimates
[33]
and adenocarcinoma; therefore, further study of for CTC. Furthermore, Mimori et al. showed that
[51]
esophageal adenocarcinoma is needed. CTCs occurred in early stages of the disease, and CTC
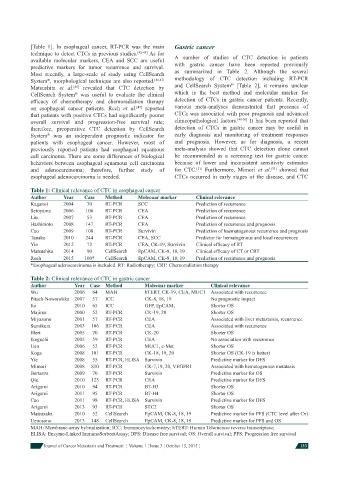
Table 1: Clinical relevance of CTC in esophageal cancer
Author Year Case Method Molecuar marker Clinical relevance
Kaganoi 2004 70 RT-PCR SCC Prediction of recurrence
Setoyama 2006 106 RT-PCR CEA Prediction of recurrence
Liu 2007 53 RT-PCR CEA Prediction of recurrence
Hashimoto 2008 147 RT-PCR CEA Prediction of recurrence and prognosis
Cao 2009 108 RT-PCR Survivin Prediction of haematogenous recurrence and prognosis
Tanaka 2010 244 RT-PCR CEA, SCC Predictor for hematogenous and local recurrences
Yin 2012 72 RT-PCR CEA, CK-19, Survivin Clinical effi cacy of RT
Matsushita 2014 90 CellSearch EpCAM, CK-8, 18, 19 Clinical effi cacy of CT or CRT
Reeh 2015 100* CellSearch EpCAM, CK-8, 18, 19 Prediction of recurrence and prognosis
*Esophageal adenocarcinoma is included. RT: Radiotherapy; CRT: Chemoradiation therapy
Table 2: Clinical relevance of CTC in gastric cancer
Author Year Case Method Molecuar marker Clinical relevance
Wu 2006 64 MAH hTERT, CK-19, CEA, MUC1 Associated with recurrence
Pituch-Noworolska 2007 57 ICC CK-8, 18, 19 No prognostic impact
Ito 2010 65 ICC GFP, EpCAM, Shorter OS
Majima 2000 52 RT-PCR CK-19, 20 Shorter OS
Miyazono 2001 57 RT-PCR CEA Associated with liver metastaisis, recurrence
Sumikura 2003 106 RT-PCR CEA Associated with recurrence
Illert 2005 70 RT-PCR CK-20 Shorter OS
Ikeguchi 2005 59 RT-PCR CEA No association with recurrence
Uen 2006 52 RT-PCR MUC1, c-Met Shorter OS
Koga 2008 101 RT-PCR CK-18, 19, 20 Shorter OS (CK-19 is better)
Yie 2008 55 RT-PCR, ELISA Survivin Predictive marker for DFS
Mimori 2008 810 RT-PCR CK-7,19, 20, VEGFR1 Associated with hematogenous metatasis
Bertazza 2009 70 RT-PCR Survivin Predictive marker for OS
Qiu 2010 123 RT-PCR CEA Predictive marker for DFS
Arigami 2010 94 RT-PCR B7-H3 Shorter OS
Arigami 2011 95 RT-PCR B7-H4 Shorter OS
Cao 2011 98 RT-PCR, ELISA Survivin Predictive marker for DFS
Arigami 2013 93 RT-PCR STC2 Shorter OS
Matsusaka 2010 52 CellSearch EpCAM, CK-8, 18, 19 Predictive marker for PFS (CTC level after Cx)
Uenosono 2013 148 CellSearch EpCAM, CK-8, 18, 19 Predictive marker for PFS and OS
MAH: Membrane-array hybrudization; ICC: Immunocytochemistry; hTERT: Human Telomerase reverse transcriptase;
ELISA: Enzyme-Linked ImmunoSorbentAssay; DFS: Disease free survival; OS: Overall survival; PFS: Progression free survival
Journal of Cancer Metastasis and Treatment ¦ Volume 1 ¦ Issue 3 ¦ October 15, 2015 ¦ 133