Page 68 - Read Online
P. 68
Lue et al. J Cancer Metastasis Treat 2022;8:11 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-4722.2021.193 Page 11 of 25
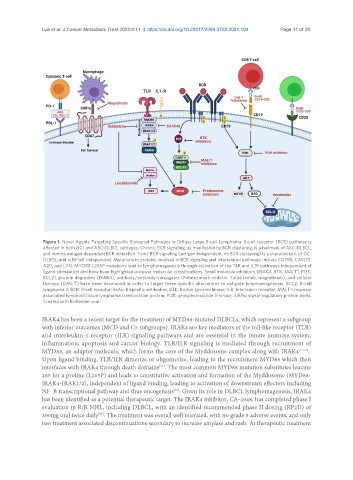
Figure 1. Novel Agents Targeting Specific Biological Pathways in Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphoma. B-cell receptor (BCR) pathway is
affected in both GC- and ABC-DLBCL subtypes. Chronic BCR signaling, as manifested by BCR clustering, is a hallmark of ABC-DLBCL,
and mimics antigen-dependent BCR activation. Tonic BCR signaling (antigen-independent, no BCR clustering) is a characteristic of GC-
DLBCL, and is NF-κB-independent. Mutations in proteins involved in BCR signaling and interrelated pathways include CD79B, CARD11,
A20, and LYN. MYD88 L265P mutations lead to lymphomagenesis through activation of the TLR and IL1R pathways independent of
ligand stimulation and have been highlighted in newer molecular classifications. Small molecule inhibitors (IRAK4, BTK, MALT1, PI3K,
BCL2), protein degraders (IRAK4), antibody/antibody-conjugates (Polatuzumab-vedotin, Tafasitamab, magrolimab), and cellular
therapy (CAR-T) have been developed in order to target these specific aberrations to mitigate lymphomagenesis. BCL2: B-cell
lymphoma 2; BCR: B-cell receptor; BsAb: Bispecific antibodies; BTK: Bruton tyrosine kinase; ILR: Interleukin receptor; MALT1: mucosa-
associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma translocation protein; PI3K: phosphoinositide 3-kinase; SIRPα: signal-regulatory protein alpha.
Created with BioRender.com.
IRAK4 has been a recent target for the treatment of MYD88-mutated DLBCLs, which represent a subgroup
with inferior outcomes (MCD and C5 subgroups). IRAKs are key mediators of the toll-like receptor (TLR)
and interleukin-1 receptor (ILR) signaling pathways and are essential in the innate immune system,
inflammation, apoptosis and cancer biology. TLR/ILR signaling is mediated through recruitment of
MYD88, an adaptor molecule, which forms the core of the Myddosome complex along with IRAK4 [71,72] .
Upon ligand binding, TLR/ILR dimerize or oligomerize, leading to the recruitment MYD88 which then
interfaces with IRAK4 through death domains . The most common MYD88 mutation substitutes leucine
[71]
265 for a proline (L265P) and leads to constitutive activation and formation of the Myddosome (MYD88-
IRAK4-IRAK1/2), independent of ligand binding, leading to activation of downstream effectors including
[73]
NF B transcriptional pathway and thus oncogenesis . Given its role in DLBCL lymphomagenesis, IRAK4
has been identified as a potential therapeutic target. The IRAK4 inhibitor, CA-4948, has completed phase I
evaluation in R/R NHL, including DLBCL, with an identified recommended phase II dosing (RP2D) of
300mg oral twice daily . The treatment was overall well tolerated, with no grade 5 adverse events, and only
[74]
two treatment associated discontinuations secondary to increase amylase and rash. At therapeutic treatment