Page 8 - Read Online
P. 8
Page 4 of 17 Testa et al. J Cancer Metastasis Treat 2020;6:53 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-4722.2020.111
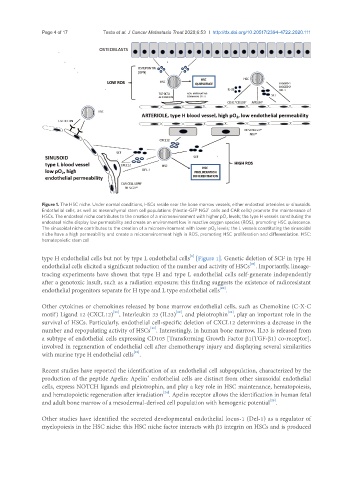
Figure 1. The HSC niche. Under normal conditions, HSCs reside near the bone marrow vessels, either endosteal arterioles or sinusoids.
+
Endothelial cells, as well as mesenchymal stem cell populations (Nestin-GFP NG2 cells and CAR cells) promote the maintenance of
HSCs. The endosteal niche contributes to the creation of a microenvironment with higher pO 2 levels; the type H vessels constituting the
endosteal niche display low permeability and create an environment low in reactive oxygen species (ROS), promoting HSC quiescence.
The sinusoidal niche contributes to the creation of a microenvironment with lower pO 2 levels; the L vessels constituting the sinusoidal
niche have a high permeability and create a microenvironment high in ROS, promoting HSC proliferation and differentiation. HSC:
hematopoietic stem cell
[6]
type H endothelial cells but not by type L endothelial cells [Figure 1]. Genetic deletion of SCF in type H
endothelial cells elicited a significant reduction of the number and activity of HSCs . Importantly, lineage-
[20]
tracing experiments have shown that type H and type L endothelial cells self-generate independently
after a genotoxic insult, such as a radiation exposure; this finding suggests the existence of radioresistant
[20]
endothelial progenitors separate for H type and L type endothelial cells .
Other cytokines or chemokines released by bone marrow endothelial cells, such as Chemokine (C-X-C
motif) Ligand 12 (CXCL12) , Interleukin 33 (IL33) , and pleiotrophin , play an important role in the
[21]
[22]
[23]
survival of HSCs. Particularly, endothelial cell-specific deletion of CXCL12 determines a decrease in the
[21]
number and repopulating activity of HSCs . Interestingly, in human bone marrow, IL33 is released from
a subtype of endothelial cells expressing CD105 [Transforming Growth Factor b1(TGF-b1) co-receptor],
involved in regeneration of endothelial cell after chemotherapy injury and displaying several similarities
[22]
with murine type H endothelial cells .
Recent studies have reported the identification of an endothelial cell subpopulation, characterized by the
production of the peptide Apelin: Apelin endothelial cells are distinct from other sinusoidal endothelial
+
cells, express NOTCH ligands and pleiotrophin, and play a key role in HSC maintenance, hematopoiesis,
and hematopoietic regeneration after irradiation . Apelin receptor allows the identification in human fetal
[24]
[25]
and adult bone marrow of a mesodermal-derived cell population with hemogenic potential .
Other studies have identified the secreted developmental endothelial locus-1 (Del-1) as a regulator of
myelopoiesis in the HSC niche: this HSC niche factor interacts with b3 integrin on HSCs and is produced