Page 58 - Read Online
P. 58
Page 6 of 10 Almeida et al. J Cancer Metastasis Treat 2021;7:57 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-4722.2021.108
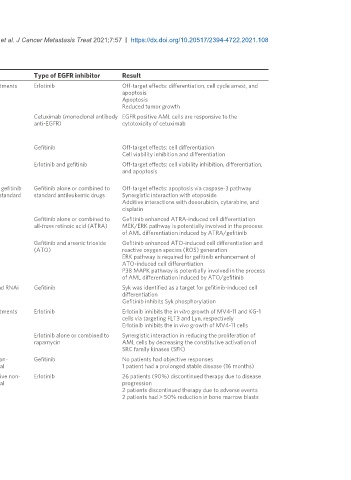
Table 1. Effects of EGFR inhibitors in AML
Study Sample Study design Type of EGFR inhibitor Result
[2]
Boehrer et al. , 2008 P39, KG-1, HL-60 EGFR negative AML cell lines In vitro and in vivo treatments Erlotinib Off-target effects: differentiation, cell cycle arrest, and
+
CD34 EGFR negative AML primary blasts apoptosis
SCID mice inoculated with KG-1 cells Apoptosis
Reduced tumor growth
[5]
Sun et al. , 2012 HL-60, HEL, Molt-4, and Hut78 EGFR negative AML cell In vitro treatment Cetuximab (monoclonal antibody EGFR positive AML cells are responsive to the
lines anti-EGFR) cytotoxicity of cetuximab
K562 and CEM EGFR positive AML cell lines
EGFR negative and positive AML primary cells
[6]
Stegmaier et al. , HL-60, Kasumi-1, U937 EGFR negative AML cell lines In vitro treatment Gefitinib Off-target effects: cell differentiation
2005 AML primary blasts Cell viability inhibition and differentiation
[7]
Boehrer et al. , 2008 P39, MOLM-13, MV4-11, U937, HL-60, KG-1 MDS In vitro treatment Erlotinib and gefitinib Off-target effects: cell viability inhibition, differentiation,
(myelodysplastic syndrome)/AML cell lines and apoptosis
+
CD34 EGFR negative MDS/AML primary blasts
[8]
Lindhagen et al. , AML primary blasts and MV4-11 EGFR negative AML cell In vitro treatment with gefitinib Gefitinib alone or combined to Off-target effects: apoptosis via caspase-3 pathway
2008 lines alone or combined to standard standard antileukemic drugs Synergistic interaction with etoposide
antileukemic drugs Additive interactions with doxorubicin, cytarabine, and
cisplatin
[13]
Miranda et al. , 2008 HL-60, NB4, U937 AML cell lines In vitro treatment Gefitinib alone or combined to Gefitinib enhanced ATRA-induced cell differentiation
all-trans retinoic acid (ATRA) MEK/ERK pathway is potentially involved in the process
of AML differentiation induced by ATRA/gefitinib
[14]
Noh et al. , 2010 NB4 AML cell line In vitro treatment Gefitinib and arsenic trioxide Gefitinib enhanced ATO-induced cell differentiation and
(ATO) reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation
ERK pathway is required for gefitinib enhancement of
ATO-induced cell differentiation
P38 MAPK pathway is potentially involved in the process
of AML differentiation induced by ATO/gefitinib
[15]
Hahn et al. , 2009 HL-60 AML cell line Mass spectrometry and RNAi Gefitinib Syk was identified as a target for gefitinib-induced cell
screening differentiation
Gefitinib inhibits Syk phosphorylation
[16]
Cao et al. , 2020 MV4-11 and KG-1 AML cell lines In vitro and in vivo treatments Erlotinib Erlotinib inhibits the in vitro growth of MV4-11 and KG-1
cells via targeting FLT3 and Lyn, respectively
Erlotinib inhibits the in vivo growth of MV4-11 cells
[17]
Boehrer et al. , 2011 KG-1, KG-1a, MOLM-13, and HL-60 AML cell lines In vitro treatment Erlotinib alone or combined to Synergistic interaction in reducing the proliferation of
rapamycin AML cells by decreasing the constitutive activation of
SRC family kinases (SFK)
[18]
Deangelo et al. , 2014 18 (11 relapsed) AML patients negative for FLT3-ITD Phase II prospective non- Gefitinib No patients had objective responses
mutation with a median age of 72 (range 57-84 years) randomized clinical trial 1 patient had a prolonged stable disease (16 months)
[19]
Abou Dalle et al. , 29 relapsed/refractory AML patients with a median age Pilot phase II prospective non- Erlotinib 26 patients (90%) discontinued therapy due to disease
2018 of 67 (range 20-83 years) randomized clinical trial progression
2 patients discontinued therapy due to adverse events
2 patients had > 50% reduction in bone marrow blasts