Page 9 - Read Online
P. 9
Page 4 of 14 Atmaja et al. J Cancer Metastasis Treat 2021;7:xx https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-4722.2021.66
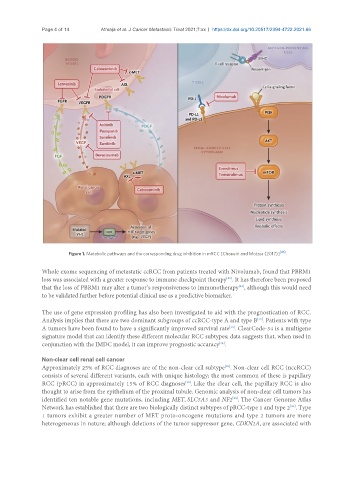
Figure 1. Metabolic pathways and the corresponding drug inhibition in mRCC [Choueiri and Motzer (2017)] [46] .
Whole exome sequencing of metastatic ccRCC from patients treated with Nivolumab, found that PBRM1
[32]
loss was associated with a greater response to immune checkpoint therapy . It has therefore been proposed
that the loss of PBRM1 may alter a tumor’s responsiveness to immunotherapy , although this would need
[32]
to be validated further before potential clinical use as a predictive biomarker.
The use of gene expression profiling has also been investigated to aid with the prognostication of RCC.
Analysis implies that there are two dominant subgroups of ccRCC-type A and type B . Patients with type
[33]
[33]
A tumors have been found to have a significantly improved survival rate . ClearCode-34 is a multigene
signature model that can identify these different molecular RCC subtypes; data suggests that, when used in
[34]
conjunction with the IMDC model, it can improve prognostic accuracy .
Non-clear cell renal cell cancer
Approximately 25% of RCC diagnoses are of the non-clear cell subtype . Non-clear cell RCC (nccRCC)
[35]
consists of several different variants, each with unique histology; the most common of these is papillary
RCC (pRCC) in approximately 15% of RCC diagnoses . Like the clear cell, the papillary RCC is also
[35]
thought to arise from the epithelium of the proximal tubule. Genomic analysis of non-clear cell tumors has
[35]
identified ten notable gene mutations, including MET, SLC5A3 and NF2 . The Cancer Genome Atlas
Network has established that there are two biologically distinct subtypes of pRCC-type 1 and type 2 . Type
[36]
1 tumors exhibit a greater number of MET proto-oncogene mutations and type 2 tumors are more
heterogeneous in nature; although deletions of the tumor suppressor gene, CDKN2A, are associated with