Page 87 - Read Online
P. 87
Corn et al. J Cancer Metastasis Treat 2021;7:41 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-4722.2021.63 Page 9 of 19
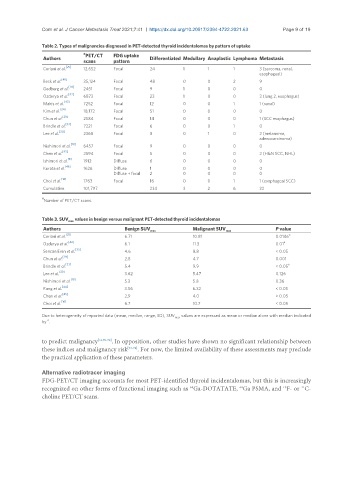
Table 2. Types of malignancies diagnosed in PET-detected thyroid incidentalomas by pattern of uptake
# PET/CT FDG uptake
Authors Differentiated Medullary Anaplastic Lymphoma Metastasis
scans pattern
[25]
Ceriani et al. 12,652 Focal 24 1 1 1 3 (sarcoma, renal,
esophageal)
[40]
Beck et al. 35,124 Focal 48 0 0 2 9
Gedberg et al. [26] 2451 Focal 9 1 0 0 0
[42]
Ozderya et al. 6873 Focal 23 1 0 0 3 (lung 2, esophagus)
[43]
Makis et al. 7252 Focal 12 0 0 1 1 (renal)
Kim et al. [24] 18,172 Focal 51 0 0 0 0
[29]
Chun et al. 2584 Focal 14 0 0 0 1 (SCC esophagus)
Brindle et al. [33] 7221 Focal 6 0 0 1 0
[30]
Lee et al. 2368 Focal 8 0 1 0 2 (melanoma,
adenocarcinoma)
[18]
Nishimori et al. 6457 Focal 9 0 0 0 0
Chen et al. [45] 2594 Focal 5 0 0 0 2 (H&N SCC, NHL)
[8]
Ishimori et al. 1912 Diffuse 6 0 0 0 0
Kurata et al. [46] 1626 Diffuse 1 0 0 0 0
Diffuse + focal 2 0 0 0 0
[16]
Choi et al. 1763 Focal 16 0 0 1 1 (esophageal SCC)
Cumulative 101,797 234 3 2 6 22
#
Number of PET/CT scans.
Table 3. SUV max values in benign versus malignant PET-detected thyroid incidentalomas
Authors Benign SUV max Malignant SUV max P value
[25] a
Ceriani et al. 6.71 10.81 0.0146
Ozderya et al. [42] 6.1 11.3 0.01 a
[35]
Sencan Eren et al. 4.6 8.8 < 0.05
[29]
Chun et al. 2.8 4.7 0.001
[33] a
Brindle et al. 5.4 9.9 < 0.05
[30]
Lee et al. 3.62 5.47 0.126
Nishimori et al. [18] 5.2 5.8 0.36
[44]
Kang et al. 3.56 6.32 < 0.05
Chen et al. [45] 2.9 4.0 > 0.05
[16]
Choi et al. 6.7 10.7 < 0.05
Due to heterogeneity of reported data (mean, median, range, SD), SUV max values are expressed as mean or median alone with median indicated
by . a
to predict malignancy [31,70-72] . In opposition, other studies have shown no significant relationship between
these indices and malignancy risk [73-76] . For now, the limited availability of these assessments may preclude
the practical application of these parameters.
Alternative radiotracer imaging
FDG-PET/CT imaging accounts for most PET-identified thyroid incidentalomas, but this is increasingly
recognized on other forms of functional imaging such as Ga-DOTATATE, Ga PSMA, and F- or C-
11
18
68
68
choline PET/CT scans.