Page 30 - Read Online
P. 30
Page 4 of 11 Heft Neal et al. J Cancer Metastasis Treat 2019;5:76 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-4722.2019.32
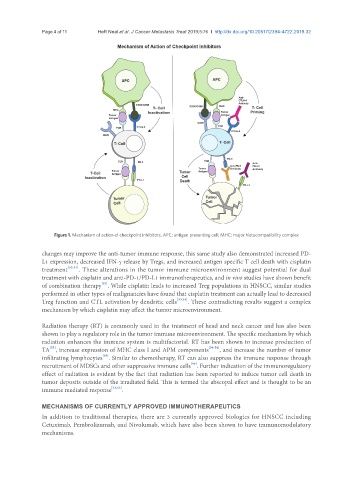
Figure 1. Mechanism of action of checkpoint inhibitors. APC: antigen presenting cell; MHC: major histocompatibility complex
changes may improve the anti-tumor immune response, this same study also demonstrated increased PD-
L1 expression, decreased IFN-γ release by Tregs, and increased antigen specific T cell death with cisplatin
treatment [52,53] . These alterations in the tumor immune microenvironment suggest potential for dual
treatment with cisplatin and anti-PD-1/PD-L1 immunotherapeutics, and in vivo studies have shown benefit
[52]
of combination therapy . While cisplatin leads to increased Treg populations in HNSCC, similar studies
performed in other types of malignancies have found that cisplatin treatment can actually lead to decreased
Treg function and CTL activation by dendritic cells [53,54] . These contradicting results suggest a complex
mechanism by which cisplatin may affect the tumor microenvironment.
Radiation therapy (RT) is commonly used in the treatment of head and neck cancer and has also been
shown to play a regulatory role in the tumor immune microenvironment. The specific mechanism by which
radiation enhances the immune system is multifactorial. RT has been shown to increase production of
[55]
TA , increase expression of MHC class I and APM components [56-58] , and increase the number of tumor
[59]
infiltrating lymphocytes . Similar to chemotherapy, RT can also suppress the immune response through
[60]
recruitment of MDSCs and other suppressive immune cells . Further indication of the immunoregulatory
effect of radiation is evident by the fact that radiation has been reported to induce tumor cell death in
tumor deposits outside of the irradiated field. This is termed the abscopal effect and is thought to be an
immune mediated response [61,62] .
MECHANISMS OF CURRENTLY APPROVED IMMUNOTHERAPEUTICS
In addition to traditional therapies, there are 3 currently approved biologics for HNSCC including
Cetuximab, Pembrolizumab, and Nivolumab, which have also been shown to have immunomodulatory
mechanisms.