Page 35 - Read Online
P. 35
Gasparello et al. J Cancer Metastasis Treat 2019;5:52 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-4722.2019.17 Page 3 of 11
A B
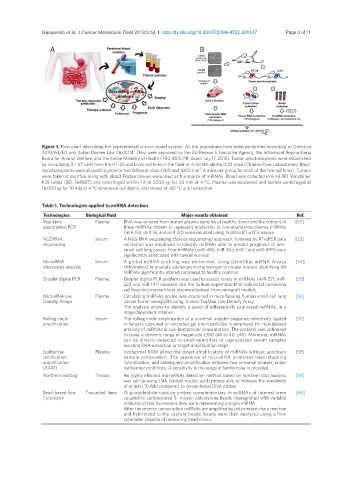
Figure 1. Flow chart describing the experimental in vivo model system. All the procedures have been performed according to Directive
2010/63/EU and Italian Decree Law 26/2014. They were approved by the EU Research Executive Agency, the Intramural Regina Elena
Board for Animal Welfare, and the Italian Ministry of Health (700-2015-PR, dated July 17, 2015). Tumor xenotransplants were established
6
by inoculating 3 × 10 cells from the HT-29 and LoVo cell lines in the flank of 4-month old Nu/CD1 mice (Charles River Laboratories, Italy).
3
Xenotransplants were allowed to grow to two different sizes (300 and 1000 mm , 6 mice per group for each of the two cell lines). Tumors
were taken at sacrifice along with blood. Frozen tissues were used as the source of miRNAs. Blood was collected in 6 mL BD Vacutainer
K2E tubes (BD, 368857) and centrifuged within 1 h at 2000 ×g for 20 min at 4 °C. Plasma was recovered and further centrifuged at
16,000 ×g for 10 min at 4 °C to remove cell debris, and stored at -80 °C until extraction
Table 1. Technologies applied to miRNA detection
Technologies Biological fluid Major results obtained Ref.
Real-time Plasma RNA was isolated from human plasma samples of healthy donor and the content of [52]
quantitative PCR three miRNAs chosen to represent moderate- to low-abundance plasma miRNAs
(miR-15b, miR-16, and miR-24) was evaluated using TaqMan RT-qPCR assays
NGS RNA Serum A NGS RNA sequencing (Solexa sequencing) approach, followed by RT-qPCR data [53]
sequencing validation was employed to identify miRNAs able to predict prognosis of non-
small-cell lung cancer. Four miRNAs (miR-486, miR-30d, miR-1 and miR-499) were
significantly associated with overall survival
MicroRNA Serum A global miRNA profiling was performed, using GeneChip miRNA Arrays [54]
microarray analysis (Affymetrix) in prostate adenocarcinoma transgenic mouse models identifying 46
miRNAs significantly altered compared to healthy controls
Droplet digital PCR Plasma Droplet digital PCR platform was used to assess levels of miRNAs (miR-221, miR- [55]
222 and miR-141) released into the culture supernatants of colorectal carcinoma
cell lines and mouse blood plasma obtained from xenograft models
MicroRNA low Plasma Circulating miRNAs profile was examined in mice bearing human small cell lung [56]
Density Arrays cancer tumor xenografts using human TaqMan Low Density Array
The analysis allows to identify a panel of differentially expressed miRNAs, in a
stage dependent manner
Rolling circle Serum The rolling circle amplification of a universal adapter sequence selectively ligated [57]
amplification to targets captured on encoded gel microparticles is employed for multiplexed
profiling of miRNAs at sub-femtomolar concentration. The protocol was optimized
to cover a dynamic range of magnitude (300 aM to 40 pM). Moreover, miRNAs
can be directly detected in small quantities of unprocessed serum samples
avoiding RNA extraction or target-amplification steps
Isothermal Plasma Isothermal RAM allows the direct amplification of miRNAs without upstream [58]
ramification sample preparation. The presence of microRNA promotes base-stacking
amplification hybridization, and subsequent amplification between two universal strands, under
(RAM) isothermal conditions. A sensitivity in the range of femtomolar is provided
Northern blotting Tissues An highly efficient microRNAs detection method based on northern blot analysis [59]
was set-up using LNA (locked nucleic acid) probes able to increase the sensitivity
of at least 10-fold compared to conventional DNA probes
Bead-based flow Tissue/cell lines Oligonucleotide-capture probes complementary to miRNAs of interest were [60]
Cytometry coupled to carboxylated 5- micron polystyrene Beads impregnated with variable
mixtures of two fluorescent dyes each representing a single miRNA
After the reverse transcription miRNAs are amplified by polymerase chain reaction
and hybridized to the capture beads, beads were then analysed using a flow
cytometer capable of measuring bead colour