Page 102 - Read Online
P. 102
Lai et al. J Cancer Metastasis Treat 2019;5:65 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-4722.2019.011 Page 5 of 9
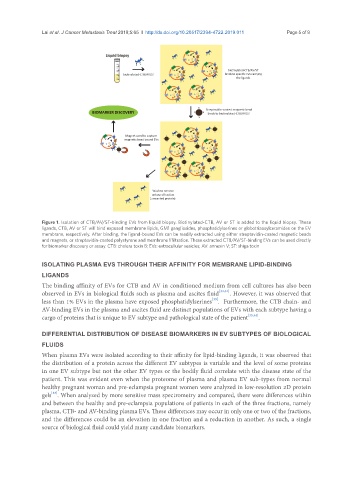
Figure 1. Isolation of CTB/AV/ST-binding EVs from liquid biopsy. Biotinylated-CTB, AV or ST is added to the liquid biopsy. These
ligands, CTB, AV or ST will bind exposed membrane lipids, GM1 gangliosides, phosphatidylserines or globotriaosylceramides on the EV
membrane, respectively. After binding, the ligand-bound EVs can be readily extracted using either streptavidin-coated magnetic beads
and magnets, or streptavidin-coated polystyrene and membrane fifiltration. These extracted CTB/AV/ST-binding EVs can be used directly
for biomarker discovery or assay. CTB: cholera toxin B; EVs: extracellular vesicles; AV: annexin V; ST: shiga toxin
ISOLATING PLASMA EVS THROUGH THEIR AFFINITY FOR MEMBRANE LIPID-BINDING
LIGANDS
The binding affinity of EVs for CTB and AV in conditioned medium from cell cultures has also been
observed in EVs in biological fluids such as plasma and ascites fluid [33,34] . However, it was observed that
[35]
less than 1% EVs in the plasma have exposed phosphatidylserines . Furthermore, the CTB chain- and
AV-binding EVs in the plasma and ascites fluid are distinct populations of EVs with each subtype having a
cargo of proteins that is unique to EV subtype and pathological state of the patient [33,34] .
DIFFERENTIAL DISTRIBUTION OF DISEASE BIOMARKERS IN EV SUBTYPES OF BIOLOGICAL
FLUIDS
When plasma EVs were isolated according to their affinity for lipid-binding ligands, it was observed that
the distribution of a protein across the different EV subtypes is variable and the level of some proteins
in one EV subtype but not the other EV types or the bodily fluid correlate with the disease state of the
patient. This was evident even when the proteome of plasma and plasma EV sub-types from normal
healthy pregnant woman and pre-eclampsia pregnant women were analyzed in low-resolution 2D protein
[33]
gels . When analyzed by more sensitive mass spectrometry and compared, there were differences within
and between the healthy and pre-eclampsia populations of patients in each of the three fractions, namely
plasma, CTB- and AV-binding plasma EVs. These differences may occur in only one or two of the fractions,
and the differences could be an elevation in one fraction and a reduction in another. As such, a single
source of biological fluid could yield many candidate biomarkers.