Page 76 - Read Online
P. 76
Page 4 of 20 Ho et al. J Cancer Metastasis Treat 2019;5:70 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-4722.2019.25
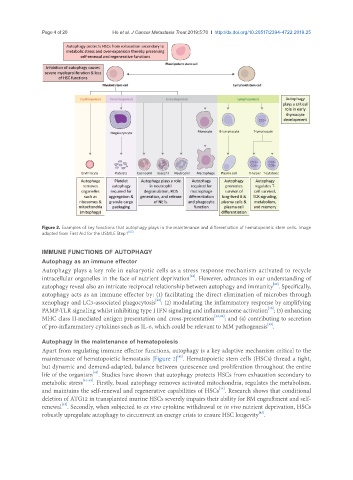
Figure 2. Examples of key functions that autophagy plays in the maintenance and differentiation of hematopoietic stem cells. Image
adapted from First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 [63]
IMMUNE FUNCTIONS OF AUTOPHAGY
Autophagy as an immune effector
Autophagy plays a key role in eukaryotic cells as a stress response mechanism activated to recycle
[38]
intracellular organelles in the face of nutrient deprivation . However, advances in our understanding of
[38]
autophagy reveal also an intricate reciprocal relationship between autophagy and immunity . Specifically,
autophagy acts as an immune effector by: (1) facilitating the direct elimination of microbes through
xenophagy and LC3-associated phagocytosis ; (2) modulating the inflammatory response by amplifying
[39]
[40]
PAMP-TLR signaling whilst inhibiting type I IFN signaling and inflammasome activation ; (3) enhancing
MHC class II-mediated antigen presentation and cross-presentation [39,40] ; and (4) contributing to secretion
[39]
of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-6, which could be relevant to MM pathogenesis .
Autophagy in the maintenance of hematopoiesis
Apart from regulating immune effector functions, autophagy is a key adaptive mechanism critical to the
[41]
maintenance of hematopoietic hemostasis [Figure 2] . Hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) thread a tight,
but dynamic and demand-adapted, balance between quiescence and proliferation throughout the entire
[41]
life of the organism . Studies have shown that autophagy protects HSCs from exhaustion secondary to
metabolic stress [41-43] . Firstly, basal autophagy removes activated mitochondria, regulates the metabolism,
[44]
and maintains the self-renewal and regenerative capabilities of HSCs . Research shows that conditional
deletion of ATG12 in transplanted murine HSCs severely impairs their ability for BM engraftment and self-
[45]
renewal . Secondly, when subjected to ex vivo cytokine withdrawal or in vivo nutrient deprivation, HSCs
robustly upregulate autophagy to circumvent an energy crisis to ensure HSC longevity .
[43]