Page 75 - Read Online
P. 75
Ho et al. J Cancer Metastasis Treat 2019;5:70 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-4722.2019.25 Page 3 of 20
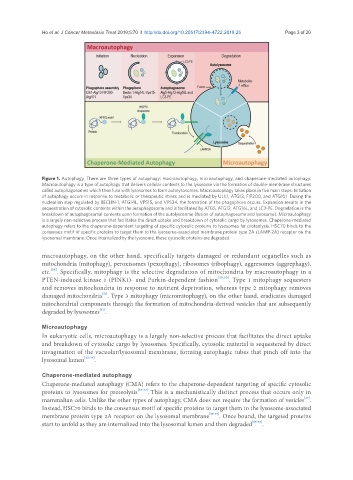
Figure 1. Autophagy. There are three types of autophagy: macroautophagy, microautophagy, and chaperone-mediated autophagy.
Macroautophagy is a type of autophagy that delivers cellular contents to the lysosome via the formation of double-membrane structures
called autophagosomes which then fuse with lysosomes to form autolysosomes. Macroautophagy takes place in five main steps. Initiation
of autophagy occurs in response to metabolic or therapeutic stress and is mediated by ULK1, ATG13, FIP200, and ATG101. During the
nucleation step regulated by BECLIN-1, ATG14L, VPS15, and VPS34, the formation of the phagophore occurs. Expansion results in the
sequestration of cytosolic contents within the autophagosome and is facilitated by ATG5, ATG12, ATG16L, and LC3-PE. Degradation is the
breakdown of autophagosomal contents upon formation of the autolysosome (fusion of autophagosome and lysosome). Microautophagy
is a largely non-selective process that facilitates the direct uptake and breakdown of cytosolic cargo by lysosomes. Chaperone-mediated
autophagy refers to the chaperone-dependent targeting of specific cytosolic proteins to lysosomes for proteolysis. HSC70 binds to the
consensus motif of specific proteins to target them to the lysosome-associated membrane protein type 2A (LAMP-2A) receptor on the
lysosomal membrane. Once internalized by the lysosome, these cytosolic proteins are degraded
macroautophagy, on the other hand, specifically targets damaged or redundant organelles such as
mitochondria (mitophagy), peroxisomes (pexophagy), ribosomes (ribophagy), aggresomes (aggrephagy),
[28]
etc. . Specifically, mitophagy is the selective degradation of mitochondria by macroautophagy in a
PTEN-induced kinase 1 (PINK1)- and Parkin-dependent fashion [29,30] . Type 1 mitophagy sequesters
and removes mitochondria in response to nutrient deprivation, whereas type 2 mitophagy removes
[31]
damaged mitochondria . Type 3 mitophagy (micromitophagy), on the other hand, eradicates damaged
mitochondrial components through the formation of mitochondria-derived vesicles that are subsequently
[31]
degraded by lysosomes .
Microautophagy
In eukaryotic cells, microautophagy is a largely non-selective process that facilitates the direct uptake
and breakdown of cytosolic cargo by lysosomes. Specifically, cytosolic material is sequestered by direct
invagination of the vacuolar/lysosomal membrane, forming autophagic tubes that pinch off into the
lysosomal lumen [32-34] .
Chaperone-mediated autophagy
Chaperone-mediated autophagy (CMA) refers to the chaperone-dependent targeting of specific cytosolic
proteins to lysosomes for proteolysis [35-37] . This is a mechanistically distinct process that occurs only in
[37]
mammalian cells. Unlike the other types of autophagy, CMA does not require the formation of vesicles .
Instead,HSC70 binds to the consensus motif of specific proteins to target them to the lysosome-associated
membrane protein type 2A receptor on the lysosomal membrane [35-37] . Once bound, the targeted proteins
start to unfold as they are internalized into the lysosomal lumen and then degraded [35-37] .