Page 52 - Read Online
P. 52
Chien et al. J Cancer Metastasis Treat 2019;5:66 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-4722.2019.016 Page 3 of 10
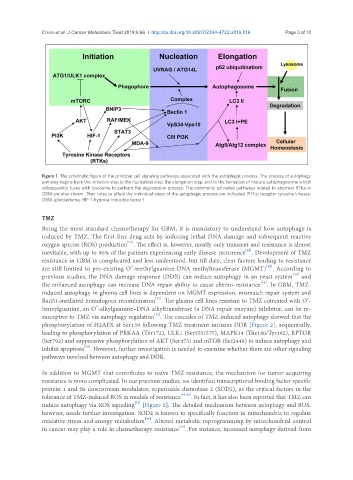
Figure 1. The schematic figure of the principal cell signaling pathways assocated with the autophagic process. The process of autophagy
pathway begins from the initiation step to the nucleation step, the elongation step, and to the formation of mature autophagosome which
subsequently fuses with lysosome to perform the degradation process. The commonly activated pathways related to aberrant RTKs in
GBM are also shown. Their roles to affect the individual steps of the autophagic process are indicated. RTKs: receptor tyrosine kinases;
GBM: glioblastoma; HIF-1: hypoxia-inducible factor-1
TMZ
Being the most standard chemotherapy for GBM, it is mandatory to understand how autophagy is
induced by TMZ. The first-line drug acts by inducing lethal DNA damage and subsequent reactive
[27]
oxygen species (ROS) production . The effect is, however, mostly only transient and resistance is almost
[28]
inevitable, with up to 90% of the patients experiencing early disease recurrence . Development of TMZ
resistance in GBM is complicated and less understood, but till date, clear factors leading to resistance
6
[29]
are still limited to pre-existing O -methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase (MGMT) . According to
[30]
previous studies, the DNA damage response (DDR) can induce autophagy in an yeast system and
[31]
the enhanced autophagy can increase DNA repair ability to cause chemo-resistance . In GBM, TMZ-
induced autophagy in glioma cell lines is dependent on MGMT expression, mismatch repair system and
[32]
6
Rad51-mediated homologous recombination . The glioma cell lines resistant to TMZ cotreated with O -
6
benzylguanine, an O -alkylguanine–DNA alkyltransferase (a DNA repair enzyme) inhibitor, can be re-
[33]
susceptive to TMZ via autophagy regulation . The cascades of TMZ-induced autophagy showed that the
phosphorylation of H2AFX at Ser139 following TMZ treatment initiates DDR [Figure 2], sequentially,
leading to phosphorylation of PRKAA (Thr172), ULK1 (Ser555/575), MAPK14 (The180/Tyr182), RPTOR
(Ser792) and suppressive phosphorylation of AKT (Ser473) and mTOR (Ser2448) to induce autophagy and
[34]
inhibit apoptosis . However, further investigation is needed to examine whether there are other signaling
pathways involved between autophagy and DDR.
In addition to MGMT that contributes to naïve TMZ resistance, the mechanism for tumor acquiring
resistance is more complicated. In our previous studies, we identified transcriptional binding factor specific
protein 1 and its downstream modulator, superoxide dismutase 2 (SOD2), as the critical factors in the
tolerance of TMZ-induced ROS in models of resistance [35,36] . In fact, it has also been reported that TMZ can
[37]
induce autophagy via ROS signaling [Figure 2]. The detailed mechanism between autophagy and ROS,
however, needs further investigation. SOD2 is known to specifically function in mitochondria to regulate
[38]
oxidative stress and energy metabolism . Altered metabolic reprogramming by mitochondrial control
in cancer may play a role in chemotherapy resistance . For instance, increased autophagy derived from
[39]