Page 61 - Read Online
P. 61
Page 10 of 15 Sawayama et al. J Cancer Metastasis Treat 2018;4:10 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-4722.2017.79
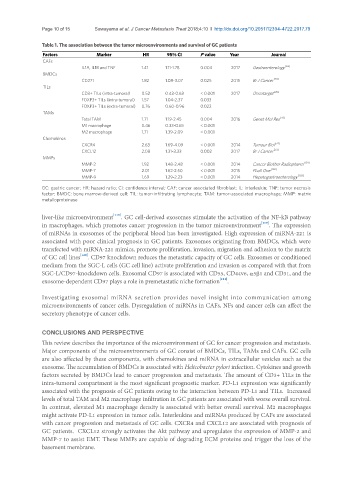
Table 1. The association between the tumor microenvironments and survival of GC patients
Factors Marker HR 95% CI P value Year Journal
CAFs
IL1A, IL1B and TNF 1.41 1.11-1.78 0.004 2017 Gastroenterology [63]
BMDCs
CD271 1.82 1.08-3.07 0.025 2015 Br J Cancer [20]
TILs
CD3+ TILs (intra-tumoral) 0.52 0.43-0.63 < 0.001 2017 Oncotarget [28]
FOXP3+ TILs (intra-tumoral) 1.57 1.04-2.37 0.033
FOXP3+ TILs (extra-tumoral) 0.76 0.60-0.96 0.022
TAMs
Total TAM 1.71 1.19-2.45 0.004 2016 Genet Mol Res [41]
M1 macrophage 0.46 0.33-0.65 < 0.001
M2 macrophage 1.71 1.39-2.09 < 0.001
Chemokines
CXCR4 2.63 1.69-4.09 < 0.001 2014 Tumour Biol [74]
CXCL12 2.08 1.31-3.33 0.002 2017 Br J Cancer [73]
MMPs
MMP-2 1.92 1.48-2.48 < 0.001 2014 Cancer Biother Radiopharm [101]
MMP-7 2.01 1.62-2.50 < 0.001 2015 PLoS One [102]
MMP-9 1.69 1.29-2.23 < 0.001 2014 Hepatogastroenterology [103]
GC: gastric cancer; HR: hazard ratio; CI: confidence interval; CAF: cancer associated fibroblast; IL: interleukin; TNF: tumor necrosis
factor; BMDC: bone marrow-derived cell; TIL: tumor-infiltrating lymphocyte; TAM: tumor-associated macrophage; MMP: matrix
metalloproteinase
liver-like microenvironment [118] . GC cell-derived exosomes stimulate the activation of the NF-kB pathway
in macrophages, which promotes cancer progression in the tumor microenvironment [119] . The expression
of miRNAs in exosomes of the peripheral blood has been investigated. High expression of miRNA-221 is
associated with poor clinical prognosis in GC patients. Exosomes originating from BMDCs, which were
transfected with miRNA-221 mimics, promote proliferation, invasion, migration and adhesion to the matrix
of GC cell lines [120] . CD97 knockdown reduces the metastatic capacity of GC cells. Exosomes or conditioned
medium from the SGC-L cells (GC cell line) activate proliferation and invasion as compared with that from
SGC-L/CD97-knockdown cells. Exosomal CD97 is associated with CD55, CD44v6, a5b1 and CD31, and the
exosome-dependent CD97 plays a role in premetastatic niche formation [121] .
Investigating exosomal miRNA secretion provides novel insight into communication among
microenvironments of cancer cells. Dysregulation of miRNAs in CAFs, NFs and cancer cells can affect the
secretory phenotype of cancer cells.
CONCLUSIONS AND PERSPECTIVE
This review describes the importance of the microenvironment of GC for cancer progression and metastasis.
Major components of the microenvironments of GC consist of BMDCs, TILs, TAMs and CAFs. GC cells
are also affected by these components, with chemokines and miRNA in extracellular vesicles such as the
exosome. The accumulation of BMDCs is associated with Helicobacter pylori infection. Cytokines and growth
factors secreted by BMDCs lead to cancer progression and metastasis. The amount of CD3+ TILs in the
intra-tumoral compartment is the most significant prognostic marker. PD-L1 expression was significantly
associated with the prognosis of GC patients owing to the interaction between PD-L1 and TILs. Increased
levels of total TAM and M2 macrophage infiltration in GC patients are associated with worse overall survival.
In contrast, elevated M1 macrophage density is associated with better overall survival. M2 macrophages
might activate PD-L1 expression in tumor cells. Interleukins and miRNAs produced by CAFs are associated
with cancer progression and metastasis of GC cells. CXCR4 and CXCL12 are associated with prognosis of
GC patients. CXCL12 strongly activates the Akt pathway and upregulates the expression of MMP-2 and
MMP-7 to assist EMT. These MMPs are capable of degrading ECM proteins and trigger the loss of the
basement membrane.