Page 54 - Read Online
P. 54
Morgan et al. HOX genes and the tumor microenvironment
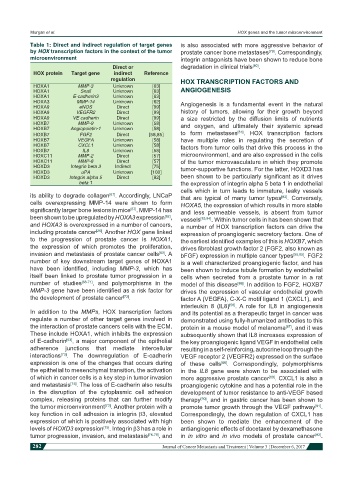
Table 1: Direct and indirect regulation of target genes is also associated with more aggressive behavior of
by HOX transcription factors in the context of the tumor prostate cancer bone metastases . Correspondingly,
[79]
microenvironment integrin antagonists have been shown to reduce bone
[80]
Direct or degradation in clinical trials .
HOX protein Target gene indirect Reference
regulation HOX TRANSCRIPTION FACTORS AND
HOXA1 MMP-3 Unknown [63]
HOXA1 Snail Unknown [63] ANGIOGENESIS
HOXA1 E-cadherin3 Unknown [63]
HOXA3 MMP-14 Unknown [62] Angiogenesis is a fundamental event in the natural
HOXA9 eNOS Direct [99]
HOXA9 VEGFR2 Direct [99] history of tumors, allowing for their growth beyond
HOXA9 VE cadherin Direct [99] a size restricted by the diffusion limits of nutrients
HOXB7 MMP-9 Unknown [58] and oxygen, and ultimately their systemic spread
HOXB7 Angiopoietin-1 Unknown [58] [81]
HOXB7 FGF2 Direct [58,85] to form metastases . HOX transcription factors
HOXB7 VEGFA Unknown [58] have multiple roles in regulating the secretion of
HOXB7 CXCL1 Unknown [58] factors from tumor cells that drive this process in the
HOXB7 IL8 Unknown [58]
HOXC11 MMP-2 Direct [57] microenvironment, and are also expressed in the cells
HOXC11 MMP-8 Direct [57] of the tumor microvasculature in which they promote
HOXD3 Integrin beta 3 Indirect [75] tumor-supportive functions. For the latter, HOXD3 has
HOXD3 uPA Unknown [100]
HOXD3 Integrin alpha 5 Direct [82] been shown to be particularly significant as it drives
beta 1 the expression of integrin alpha 5 beta 1 in endothelial
cells which in turn leads to immature, leaky vessels
its ability to degrade collagen . Accordingly, LNCaP that are typical of many tumor types . Conversely,
[67]
[82]
cells overexpressing MMP-14 were shown to form HOXA5, the expression of which results in more stable
significantly larger bone lesions in mice . MMP-14 has and less permeable vessels, is absent from tumor
[67]
been shown to be upregulated by HOXA3 expression , vessels [83,84] . Within tumor cells in has been shown that
[62]
and HOXA3 is overexpressed in a number of cancers, a number of HOX transcription factors can drive the
including prostate cancer . Another HOX gene linked expression of proangiogenic secretory factors. One of
[25]
to the progression of prostate cancer is HOXA1, the earliest identified examples of this is HOXB7, which
the expression of which promotes the proliferation, drives fibroblast growth factor 2 (FGF2, also known as
invasion and metastasis of prostate cancer cells . A bFGF) expression in multiple cancer types [58,85] . FGF2
[63]
number of key downstream target genes of HOXA1 is a well characterized proangiogenic factor, and has
have been identified, including MMP-3, which has been shown to induce tubule formation by endothelial
itself been linked to prostate tumor progression in a cells when secreted from a prostate tumor in a rat
number of studies [68-71] , and polymorphisms in the model of this disease . In addition to FGF2, HOXB7
[86]
MMP-3 gene have been identified as a risk factor for drives the expression of vascular endothelial growth
the development of prostate cancer . factor A (VEGFA), C-X-C motif ligand 1 (CXCL1), and
[72]
interleukin 8 (IL8) . A role for IL8 in angiogenesis
[58]
In addition to the MMPs, HOX transcription factors and its potential as a therapeutic target in cancer was
regulate a number of other target genes involved in demonstrated using fully-humanized antibodies to this
the interaction of prostate cancers cells with the ECM. protein in a mouse model of melanoma , and it was
[87]
These include HOXA1, which inhibits the expression subsequently shown that IL8 increases expression of
of E-cadherin , a major component of the epithelial the key proangiogenic ligand VEGF in endothelial cells
[63]
adherence junctions that mediate intercellular resulting in a self-reinforcing, autocrine loop through the
interactions . The downregulation of E-cadherin VEGF receptor 2 (VEGFR2) expressed on the surface
[73]
expression is one of the changes that occurs during of these cells . Correspondingly, polymorphisms
[88]
the epithelial to mesenchymal transition, the activation in the IL8 gene were shown to be associated with
of which in cancer cells is a key step in tumor invasion more aggressive prostate cancer . CXCL1 is also a
[89]
and metastasis . The loss of E-cadherin also results proangiogenic cytokine and has a potential role in the
[74]
in the disruption of the cytoplasmic cell adhesion development of tumor resistance to anti-VEGF based
complex, releasing proteins that can further modify therapy , and in gastric cancer has been shown to
[90]
the tumor microenvironment . Another protein with a promote tumor growth through the VEGF pathway .
[73]
[91]
key function in cell adhesion is integrin β3, elevated Correspondingly, the down regulation of CXCL1 has
expression of which is positively associated with high been shown to mediate the enhancement of the
levels of HOXD3 expression . Integrin β3 has a role in antiangiogenic effects of docetaxel by dexamethasone
[75]
tumor progression, invasion, and metastasis [76-78] , and in in vitro and in vivo models of prostate cancer .
[92]
282 Journal of Cancer Metastasis and Treatment ¦ Volume 3 ¦ December 6, 2017