Page 85 - Read Online
P. 85
Page 183 Yu et al. Intell Robot 2022;2:180-99 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/ir.2022.10
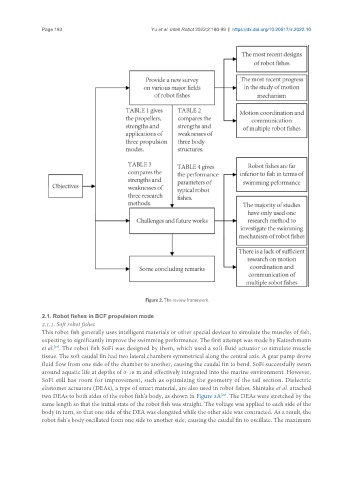
Figure 2. The review framework.
2.1. Robot fishes in BCF propulsion mode
2.1.1. Soft robot fishes
This robot fish generally uses intelligent materials or other special devices to simulate the muscles of fish,
expecting to significantly improve the swimming performance. The first attempt was made by Katzschmann
et al. . The robot fish SoFi was designed by them, which used a soft fluid actuator to simulate muscle
[19]
tissue. The soft caudal fin had two lateral chambers symmetrical along the central axis. A gear pump drove
fluid flow from one side of the chamber to another, causing the caudal fin to bend. SoFi successfully swam
around aquatic life at depths of 0-18 m and effectively integrated into the marine environment. However,
SoFi still has room for improvement, such as optimizing the geometry of the tail section. Dielectric
elastomer actuators (DEAs), a type of smart material, are also used in robot fishes. Shintake et al. attached
[20]
two DEAs to both sides of the robot fish’s body, as shown in Figure 3A . The DEAs were stretched by the
same length so that the initial state of the robot fish was straight. The voltage was applied to each side of the
body in turn, so that one side of the DEA was elongated while the other side was contracted. As a result, the
robot fish’s body oscillated from one side to another side, causing the caudal fin to oscillate. The maximum