Page 19 - Read Online
P. 19
Page 112 Wu. Intell Robot 2021;1(2):99-115 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/ir.2021.11
numerical simulation experimental measurement
2 1.5
1.5
1
1 [rad] 1 2 [rad]
0.5
0.5
0 0
0 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 0 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5
time [sec] time [sec]
0 3
2.8
-0.2
3 [rad] -0.4 5 [rad] 2.6
2.4
-0.6
2.2
-0.8 2
0 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 0 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5
time [sec] time [sec]
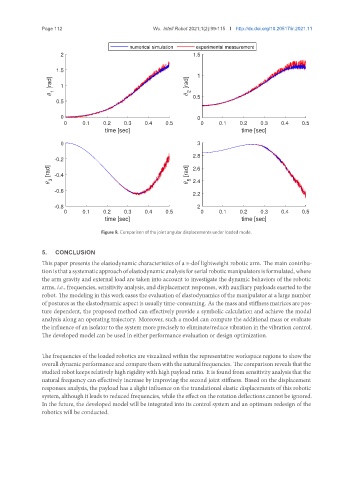
Figure 9. Comparison of the joint angular displacements under loaded mode.
5. CONCLUSION
This paper presents the elastodynamic characteristics of a 5-dof lightweight robotic arm. The main contribu-
tionisthatasystematicapproachofelastodynamicanalysisforserialroboticmanipulatorsisformulated, where
the arm gravity and external load are taken into account to investigate the dynamic behaviors of the robotic
arms, i.e., frequencies, sensitivity analysis, and displacement responses, with auxiliary payloads exerted to the
robot. The modeling in this work eases the evaluation of elastodynamics of the manipulator at a large number
of postures as the elastodynamic aspect is usually time-consuming. As the mass and stiffness matrices are pos-
ture dependent, the proposed method can effectively provide a symbolic calculation and achieve the modal
analysis along an operating trajectory. Moreover, such a model can compute the additional mass or evaluate
the influence of an isolator to the system more precisely to eliminate/reduce vibration in the vibration control.
The developed model can be used in either performance evaluation or design optimization.
The frequencies of the loaded robotics are visualized within the representative workspace regions to show the
overalldynamicperformanceandcomparethemwiththenaturalfrequencies. Thecomparisonrevealsthatthe
studied robot keeps relatively high rigidity with high payload ratio. It is found from sensitivity analysis that the
natural frequency can effectively increase by improving the second joint stiffness. Based on the displacement
responses analysis, the payload has a slight influence on the translational elastic displacements of this robotic
system, although it leads to reduced frequencies, while the effect on the rotation deflections cannot be ignored.
In the future, the developed model will be integrated into its control system and an optimum redesign of the
robotics will be conducted.