Page 78 - Read Online
P. 78
Page 73 Li et al. Intell Robot 2021;1(1):58-83 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/ir.2021.08
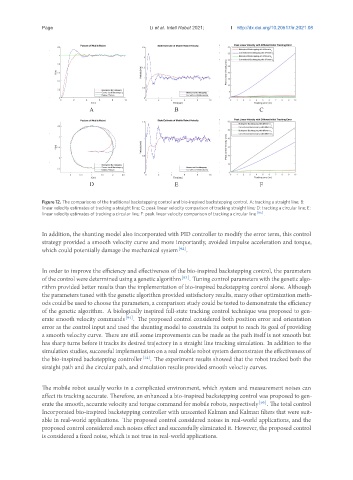
Figure 12. The comparisons of the traditional backstepping control and bio-inspired backstepping control. A: tracking a straight line; B:
linear velocity estimates of tracking a straight line; C: peak linear velocity comparison of tracking straight line; D: tracking a circular line; E:
linear velocity estimates of tracking a circular line; F: peak linear velocity comparison of tracking a circular line [95] .
In addition, the shunting model also incorporated with PID controller to modify the error term, this control
strategy provided a smooth velocity curve and more importantly, avoided impulse acceleration and torque,
which could potentially damage the mechanical system [92] .
In order to improve the efficiency and effectiveness of the bio-inspired backstepping control, the parameters
of the control were determined using a genetic algorithm [93] . Tuning control parameters with the genetic algo-
rithm provided better results than the implementation of bio-inspired backstepping control alone. Although
the parameters tuned with the genetic algorithm provided satisfactory results, many other optimization meth-
ods could be used to choose the parameters, a comparison study could be tested to demonstrate the efficiency
of the genetic algorithm. A biologically inspired full-state tracking control technique was proposed to gen-
erate smooth velocity commands [94] . The proposed control considered both position error and orientation
error as the control input and used the shunting model to constrain its output to reach its goal of providing
a smooth velocity curve. There are still some improvements can be made as the path itself is not smooth but
has sharp turns before it tracks its desired trajectory in a straight line tracking simulation. In addition to the
simulation studies, successful implementation on a real mobile robot system demonstrates the effectiveness of
the bio-inspired backstepping controller [14] . The experiment results showed that the robot tracked both the
straight path and the circular path, and simulation results provided smooth velocity curves.
The mobile robot usually works in a complicated environment, which system and measurement noises can
affect its tracking accurate. Therefore, an enhanced a bio-inspired backstepping control was proposed to gen-
erate the smooth, accurate velocity and torque command for mobile robots, respectively [95] . The total control
Incorporated bio-inspired backstepping controller with unscented Kalman and Kalman filters that were suit-
able in real-world applications. The proposed control considered noises in real-world applications, and the
proposed control considered such noises effect and successfully eliminated it. However, the proposed control
is considered a fixed noise, which is not true in real-world applications.