Page 75 - Read Online
P. 75
Page 259 Liu et al. Intell Robot 2024;4(3):256-75 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/ir.2024.17
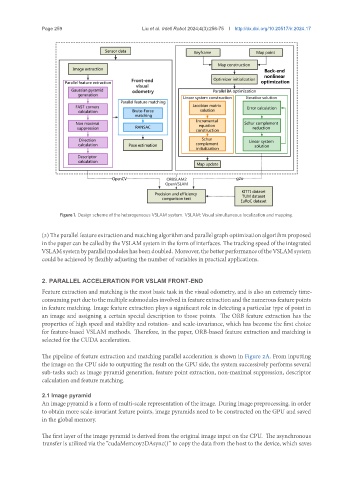
Figure 1. Design scheme of the heterogeneous VSLAM system. VSLAM: Visual simultaneous localization and mapping.
(3)Theparallelfeatureextractionandmatchingalgorithmandparallelgraphoptimizationalgorithmproposed
in the paper can be called by the VSLAM system in the form of interfaces. The tracking speed of the integrated
VSLAMsystembyparallelmoduleshasbeendoubled. Moreover,thebetterperformanceoftheVSLAMsystem
could be achieved by flexibly adjusting the number of variables in practical applications.
2. PARALLEL ACCELERATION FOR VSLAM FRONT-END
Feature extraction and matching is the most basic task in the visual odometry, and is also an extremely time-
consumingpartduetothemultiplesubmodulesinvolvedinfeatureextractionandthenumerousfeaturepoints
in feature matching. Image feature extraction plays a significant role in detecting a particular type of point in
an image and assigning a certain special description to those points. The ORB feature extraction has the
properties of high speed and stability and rotation- and scale-invariance, which has become the first choice
for feature-based VSLAM methods. Therefore, in the paper, ORB-based feature extraction and matching is
selected for the CUDA acceleration.
The pipeline of feature extraction and matching parallel acceleration is shown in Figure 2A. From inputting
the image on the CPU side to outputting the result on the GPU side, the system successively performs several
sub-tasks such as image pyramid generation, feature point extraction, non-maximal suppression, descriptor
calculation and feature matching.
2.1 Image pyramid
An image pyramid is a form of multi-scale representation of the image. During image preprocessing, in order
to obtain more scale-invariant feature points, image pyramids need to be constructed on the GPU and saved
in the global memory.
The first layer of the image pyramid is derived from the original image input on the CPU. The asynchronous
transfer is utilized via the “cudaMemcoy2DAsync()” to copy the data from the host to the device, which saves