Page 333 - Read Online
P. 333
Page 10 of 17 Shrestha et al. Hepatoma Res 2019;5:32 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-5079.2019.24
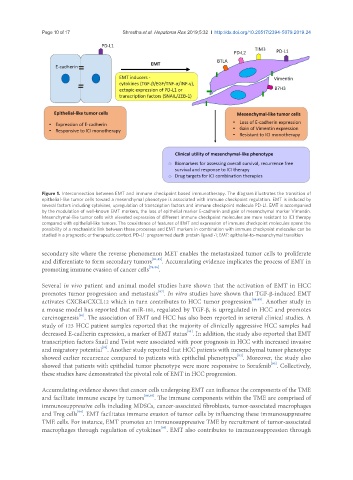
Figure 1. Interconnection between EMT and immune checkpoint based immunotherapy. The diagram illustrates the transition of
epithelial-like tumor cells toward a mesenchymal phenotype is associated with immune checkpoint regulation. EMT is induced by
several factors including cytokines, upregulation of transcription factors and immune checkpoint molecule PD-L1. EMT is accompanied
by the modulation of well-known EMT markers, the loss of epithelial marker E-cadherin and gain of mesenchymal marker Vimentin.
Mesenchymal-like tumor cells with elevated expression of different immune checkpoint molecules are more resistant to ICI therapy
compared with epithelial-like tumors. The coexistence of features of EMT and expression of immune checkpoint molecules opens the
possibility of a mechanistic link between these processes and EMT markers in combination with immune checkpoint molecules can be
studied in a prognostic or therapeutic context. PD-L1: programmed death protein ligand -1; EMT: epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition
secondary site where the reverse phenomenon MET enables the metastasized tumor cells to proliferate
and differentiate to form secondary tumors [84,85] . Accumulating evidence implicates the process of EMT in
promoting immune evasion of cancer cells [78,86] .
Several in vivo patient and animal model studies have shown that the activation of EMT in HCC
[87]
promotes tumor progression and metastasis . In vitro studies have shown that TGF-β-induced EMT
activates CXCR4/CXCL12 which in turn contributes to HCC tumor progression [88,89] . Another study in
a mouse model has reported that miR-181, regulated by TGF-β, is upregulated in HCC and promotes
[90]
carcinogenesis . The association of EMT and HCC has also been reported in several clinical studies. A
study of 123 HCC patient samples reported that the majority of clinically aggressive HCC samples had
[91]
decreased E-cadherin expression, a marker of EMT status . In addition, the study also reported that EMT
transcription factors Snail and Twist were associated with poor prognosis in HCC with increased invasive
[91]
and migratory potential . Another study reported that HCC patients with mesenchymal tumor phenotype
showed earlier recurrence compared to patients with epithelial phenotypes . Moreover, the study also
[92]
[92]
showed that patients with epithelial tumor phenotype were more responsive to Sorafenib . Collectively,
these studies have demonstrated the pivotal role of EMT in HCC progression.
Accumulating evidence shows that cancer cells undergoing EMT can influence the components of the TME
and facilitate immune escape by tumors [86,93] . The immune components within the TME are comprised of
immunosuppressive cells including MDSCs, cancer-associated fibroblasts, tumor-associated macrophages
[94]
and Treg cells . EMT facilitates immune evasion of tumor cells by influencing these immunosuppressive
TME cells. For instance, EMT promotes an immunosuppressive TME by recruitment of tumor-associated
[95]
macrophages through regulation of cytokines . EMT also contributes to immunosuppression through