Page 256 - Read Online
P. 256
Page 6 of 9 Bose et al. Hepatoma Res 2019;5:24 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-5079.2019.10
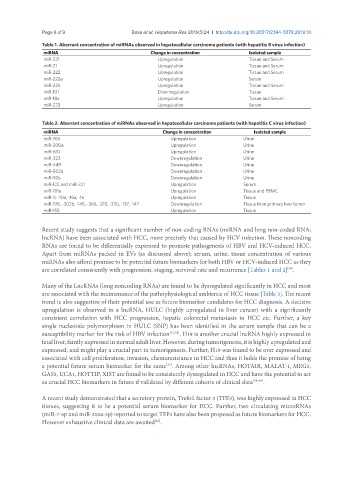
Table 1. Aberrant concentration of miRNAs observed in hepatocellular carcinoma patients (with hepatitis B virus infection)
miRNA Change in concentration Isolated sample
miR-221 Upregulation Tissue and Serum
miR-21 Upregulation Tissue and Serum
miR-222 Upregulation Tissue and Serum
miR-222a Upregulation Serum
miR-224 Upregulation Tissue and Serum
miR-101 Downregulation Tissue
miR-18a Upregulation Tissue and Serum
miR-223 Upregulation Serum
Table 2. Aberrant concentration of miRNAs observed in hepatocellular carcinoma patients (with hepatitis C virus infection)
miRNA Change in concentration Isolated sample
miR-765 Upregulation Urine
miR-200a Upregulation Urine
miR-610 Upregulation Urine
miR-323 Downregulation Urine
miR-449 Downregulation Urine
miR-502d Downregulation Urine
miR-92b Downregulation Urine
miR-122 and miR-221 Upregulation Serum
miR-181a Upregulation Tissue and PBMC
miR-9, -10a, -15a, -16 Upregulation Tissue
miR-198, -302b, -145, -368, -218, -330, -137, -147 Downregulation Tissue from primary liver tumor
miR-155 Upregulation Tissue
Recent study suggests that a significant number of non-coding RNAs (miRNA and long non-coded RNA;
lncRNA) have been associated with HCC, more precisely that caused by HCV infection. These noncoding
RNAs are found to be differentially expressed to promote pathogenesis of HBV and HCV-induced HCC.
Apart from miRNAs packed in EVs (as discussed above); serum, urine, tissue concentration of various
miRNAs also afford promise to be potential future biomarkers for both HBV or HCV-induced HCC as they
are correlated consistently with progression, staging, survival rate and recurrence [Tables 1 and 2] .
[30]
Many of the LncRNAs (long noncoding RNAs) are found to be dysregulated significantly in HCC and most
are associated with the maintenance of the pathophysiological ambience of HCC tissue [Table 3]. The recent
trend is also suggestive of their potential use as future biomarker candidates for HCC diagnosis. A decisive
upregulation is observed in a lncRNA, HULC (highly upregulated in liver cancer) with a significantly
consistent correlation with HCC progression, hepatic colorectal metastasis in HCC etc. Further, a key
single nucleotide polymorphism in HULC (SNP) has been identified in the serum sample that can be a
susceptibility marker for the risk of HBV infection [31,32] . H19 is another crucial lncRNA highly expressed in
fetal liver, faintly expressed in normal adult liver. However, during tumorigenesis, it is highly upregulated and
expressed, and might play a crucial part in tumorigenesis. Further, H19 was found to be over expressed and
associated with cell proliferation, invasion, chemoresistance in HCC and thus it holds the promise of being
a potential future serum biomarker for the same . Among other lncRNAs, HOTAIR, MALAT-1, MEG3,
[33]
GAS5, UCA1, HOTTIP, XIST are found to be consistently dysregulated in HCC and have the potential to act
as crucial HCC biomarkers in future if validated by different cohorts of clinical data [34-40] .
A recent study demonstrated that a secretory protein, Trefoil factor 3 (TFF3), was highly expressed in HCC
tissues, suggesting it to be a potential serum biomarker for HCC. Further, two circulating microRNAs
(miR-7-5p and miR-203a-3p) reported to target TFF3 have also been proposed as future biomarkers for HCC.
However exhaustive clinical data are awaited .
[41]