Page 103 - Read Online
P. 103
Ma et al. Hepatoma Res 2019;5:8 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-5079.2018.104 Page 7 of 12
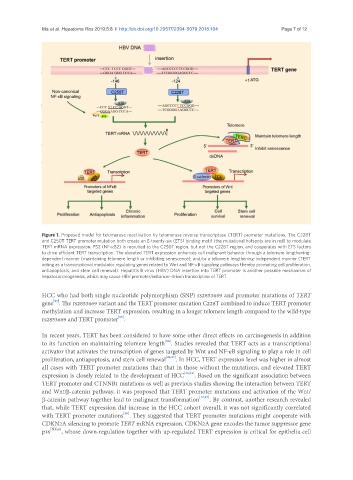
Figure 1. Proposed model for telomerase reactivation by telomerase reverse transcriptase (TERT) promoter mutations. The C228T
and C250T TERT promoter mutation both create an E-twenty-six (ETS) binding motif (the mutational hotspots are in red) to modulate
TERT mRNA expression. P52 (NF-κB2) is recruited to the C250T region, but not the C228T region, and cooperates with ETS factors
to drive efficient TERT transcription. The elevated TERT expression enhances cell malignant behavior through a telomere lengthening-
dependent manner (maintaining telomere length or inhibiting senescence), and/or a telomere lengthening-independent manner (TERT
acting as a transcriptional modulator regulating genes related to Wnt and NF-κB signaling pathways thereby promoting cell proliferation,
antiapoptosis, and stem cell renewal). Hepatitis B virus (HBV) DNA insertion into TERT promoter is another possible mechanism of
hepatocarcinogenesis, which may cause HBV promoter/enhancer-driven transcription of TERT
HCC who had both single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) rs2853669 and promoter mutations of TERT
[95]
gene . The rs2853669 variant and the TERT promoter mutation C228T combined to induce TERT promoter
methylation and increase TERT expression, resulting in a longer telomere length compared to the wild-type
[95]
rs2853669 and TERT promoter .
In recent years, TERT has been considered to have some other direct effects on carcinogenesis in addition
[96]
to its function on maintaining telomere length . Studies revealed that TERT acts as a transcriptional
activator that activates the transcription of genes targeted by Wnt and NF-κB signaling to play a role in cell
proliferation, antiapoptosis, and stem cell renewal [96,97] . In HCC, TERT expression level was higher in almost
all cases with TERT promoter mutations than that in those without the mutations, and elevated TERT
expression is closely related to the development of HCC [42,94] . Based on the significant association between
TERT promoter and CTNNB1 mutations as well as previous studies showing the interaction between TERT
and Wnt/β-catenin pathway, it was proposed that TERT promoter mutations and activation of the Wnt/
β-catenin pathway together lead to malignant transformation [42,97] . By contrast, another research revealed
that, while TERT expression did increase in the HCC cohort overall, it was not significantly correlated
[48]
with TERT promoter mutations . They suggested that TERT promoter mutations might cooperate with
CDKN2A silencing to promote TERT mRNA expression. CDKN2A gene encodes the tumor suppressor gene
p16 INK4A , whose down-regulation together with up-regulated TERT expression is critical for epithelia cell