Page 303 - Read Online
P. 303
Martini et al. Hepatoma Res 2018;4:28 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-5079.2018.50 Page 3 of 9
Chronic inflammation, oxidative stress, iron overload, hypoxia
Kato [15] ,1996
Cannito et al. [18] , 2015
Turato et al. [19] , 2018
Ras-associated cytokine production
Catanzaro et al. [28] , 2014
TGF-β and fibrosis
Apoptosis Turato et al. [40] , 2010
Ciscato et al. [24] , 2014 Novo et al. [43] , 2017
Proliferation
Quarta et al. [25] , 2010
EMT and cellular Invasion
MYC oncogene Quarta et al. [25] , 2010
Turato et al. [27] , 2015
Hepatocellular carcinoma
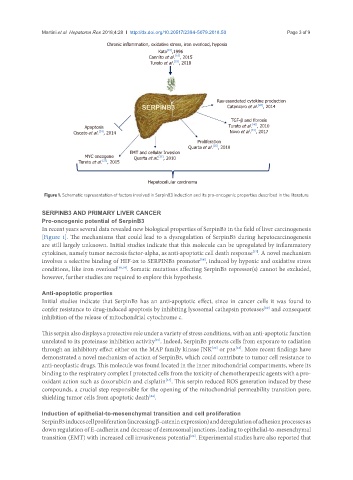
Figure 1. Schematic rapresentation of factors involved in SerpinB3 induction and its pro-oncogenic properties described in the literature
SERPINB3 AND PRIMARY LIVER CANCER
Pro-oncogenic potential of SerpinB3
In recent years several data revealed new biological properties of SerpinB3 in the field of liver carcinogenesis
[Figure 1]. The mechanisms that could lead to a dysregulation of SerpinB3 during hepatocarcinogenesis
are still largely unknown. Initial studies indicate that this molecule can be upregulated by inflammatory
cytokines, namely tumor necrosis factor-alpha, as anti-apoptotic cell death response . A novel mechanism
[17]
involves a selective binding of HIF-2α to SERPINB3 promoter , induced by hypoxic and oxidative stress
[18]
conditions, like iron overload [18,19] . Somatic mutations affecting SerpinB3 repressor(s) cannot be excluded,
however, further studies are required to explore this hypothesis.
Anti-apoptotic properties
Initial studies indicate that SerpinB3 has an anti-apoptotic effect, since in cancer cells it was found to
confer resistance to drug-induced apoptosis by inhibiting lysosomal cathepsin proteases and consequent
[20]
inhibition of the release of mitochondrial cytochrome c.
This serpin also displays a protective role under a variety of stress conditions, with an anti-apoptotic function
unrelated to its proteinase inhibition activity . Indeed, SerpinB3 protects cells from exposure to radiation
[21]
through an inhibitory effect either on the MAP family kinase JNK or p38 . More recent findings have
[23]
[22]
demonstrated a novel mechanism of action of SerpinB3, which could contribute to tumor cell resistance to
anti-neoplastic drugs. This molecule was found located in the inner mitochondrial compartments, where its
binding to the respiratory complex I protected cells from the toxicity of chemotherapeutic agents with a pro-
oxidant action such as doxorubicin and cisplatin . This serpin reduced ROS generation induced by these
[24]
compounds, a crucial step responsible for the opening of the mitochondrial permeability transition pore,
shielding tumor cells from apoptotic death .
[24]
Induction of epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and cell proliferation
SerpinB3 induces cell proliferation (increasing β-catenin expression) and deregulation of adhesion processes as
down regulation of E-cadherin and decrease of desmosomal junctions, leading to epithelial-to-mesenchymal
transition (EMT) with increased cell invasiveness potential . Experimental studies have also reported that
[25]