Page 30 - Read Online
P. 30
Ratti et al. Fast-track management in patients with HCC
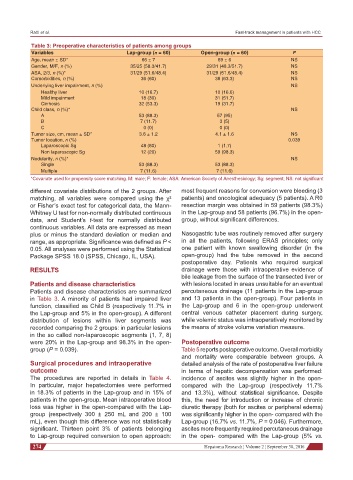
Table 3: Preoperative characteristics of patients among groups
Variables Lap-group (n = 60) Open-group (n = 60) P
Age, mean ± SD* 66 ± 7 69 ± 6 NS
Gender, M/F, n (%) 35/25 (58.3/41.7) 29/31 (48.3/51.7) NS
ASA, 2/3, n (%)* 31/29 (51.6/48.4) 31/29 (51.6/48.4) NS
Comorbidities, n (%) 36 (60) 38 (63.3) NS
Underlying liver impairment, n (%) NS
Healthy liver 10 (16.7) 10 (16.6)
Mild impairment 18 (30) 31 (51.7)
Cirrhosis 32 (53.3) 19 (31.7)
Child class, n (%)* NS
A 53 (88.3) 57 (95)
B 7 (11.7) 3 (5)
C 0 (0) 0 (0)
Tumor size, cm, mean ± SD* 3.6 ± 1.2 4.1 ± 1.6 NS
Tumor location, n (%) 0.039
Laparoscopic Sg 48 (80) 1 (1.7)
Non laparoscopic Sg 12 (20) 59 (98.3)
Nodularity, n (%)* NS
Single 53 (88.3) 53 (88.3)
Multiple 7 (11.6) 7 (11.6)
*Covariate used for propensity score matching. M: male; F: female; ASA: American Society of Anesthesiology; Sg: segment; NS: not significant
different covariate distributions of the 2 groups. After most frequent reasons for conversion were bleeding (3
matching, all variables were compared using the χ 2 patients) and oncological adequacy (5 patients). A R0
or Fisher’s exact test for categorical data, the Mann- resection margin was obtained in 59 patients (98.3%)
Whitney U test for non-normally distributed continuous in the Lap-group and 58 patients (96.7%) in the open-
data, and Student’s t-test for normally distributed group, without significant differences.
continuous variables. All data are expressed as mean
plus or minus the standard deviation or median and Nasogastric tube was routinely removed after surgery
range, as appropriate. Significance was defined as P < in all the patients, following ERAS principles; only
0.05. All analyses were performed using the Statistical one patient with known swallowing disorder (in the
Package SPSS 18.0 (SPSS, Chicago, IL, USA). open-group) had the tube removed in the second
postoperative day. Patients who required surgical
RESULTS drainage were those with intraoperative evidence of
bile leakage from the surface of the transected liver or
Patients and disease characteristics with lesions located in areas unsuitable for an eventual
Patients and disease characteristics are summarized percutaneous drainage (11 patients in the Lap-group
in Table 3. A minority of patients had impaired liver and 13 patients in the open-group). Four patients in
function, classified as Child B (respectively 11.7% in the Lap-group and 6 in the open-group underwent
the Lap-group and 5% in the open-group). A different central venous catheter placement during surgery,
distribution of lesions within liver segments was while volemic status was intraoperatively monitored by
recorded comparing the 2 groups: in particular lesions the means of stroke volume variation measure.
in the so called non-laparoscopic segments (1, 7, 8)
were 20% in the Lap-group and 98.3% in the open- Postoperative outcome
group (P = 0.039). Table 5 reports postoperative outcome. Overall morbidity
and mortality were comparable between groups. A
Surgical procedures and intraoperative detailed analysis of the rate of postoperative liver failure
outcome in terms of hepatic decompensation was performed:
The procedures are reported in details in Table 4. incidence of ascites was slightly higher in the open-
In particular, major hepatectomies were performed compared with the Lap-group (respectively 11.7%
in 18.3% of patients in the Lap-group and in 15% of and 13.3%), without statistical significance. Despite
patients in the open-group. Mean intraoperative blood this, the need for introduction or increase of chronic
loss was higher in the open-compared with the Lap- diuretic therapy (both for ascites or peripheral edema)
group (respectively 300 ± 250 mL and 200 ± 100 was significantly higher in the open- compared with the
mL), even though this difference was not statistically Lap-group (16.7% vs. 11.7%, P = 0.046). Furthermore,
significant. Thirteen point 3% of patients belonging ascites more frequently required percutaneous drainage
to Lap-group required conversion to open approach: in the open- compared with the Lap-group (5% vs.
274 Hepatoma Research ¦ Volume 2 ¦ September 30, 2016