Page 15 - Read Online
P. 15
Otsuka et al. Indications and technique for LLR in HCC with liver cirrhosis
A B C
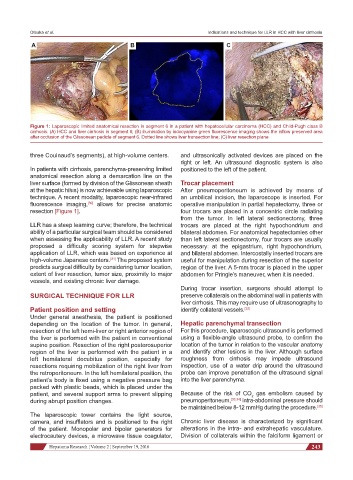
Figure 1: Laparoscopic limited anatomical resection in segment 6 in a patient with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and Child-Pugh class B
cirrhosis. (A) HCC and liver cirrhosis in segment 6; (B) illumination by indocyanine green fluorescence imaging shows the inflow preserved area
after occlusion of the Glissonean pedicle of segment 6. Dotted line shows liver transection line; (C) liver resection plane
three Couinaud’s segments), at high-volume centers. and ultrasonically activated devices are placed on the
right or left. An ultrasound diagnostic system is also
In patients with cirrhosis, parenchyma-preserving limited positioned to the left of the patient.
anatomical resection along a demarcation line on the
liver surface (formed by division of the Glissonean sheath Trocar placement
at the hepatic hilus) is now achievable using laparoscopic After pneumoperitoneum is achieved by means of
technique. A recent modality, laparoscopic near-infrared an umbilical incision, the laparoscope is inserted. For
fluorescence imaging, allows for precise anatomic operative manipulation in partial hepatectomy, three or
[30]
resection [Figure 1]. four trocars are placed in a concentric circle radiating
from the tumor. In left lateral sectionectomy, three
LLR has a steep learning curve; therefore, the technical trocars are placed at the right hypochondrium and
ability of a particular surgical team should be considered bilateral abdomen. For anatomical hepatectomies other
when assessing the applicability of LLR. A recent study than left lateral sectionectomy, four trocars are usually
proposed a difficulty scoring system for stepwise necessary: at the epigastrium, right hypochondrium,
application of LLR, which was based on experience at and bilateral abdomen. Intercostally inserted trocars are
high-volume Japanese centers. The proposed system useful for manipulation during resection of the superior
[31]
predicts surgical difficulty by considering tumor location, region of the liver. A 5-mm trocar is placed in the upper
extent of liver resection, tumor size, proximity to major abdomen for Pringle’s maneuver, when it is needed.
vessels, and existing chronic liver damage.
During trocar insertion, surgeons should attempt to
SURGICAL TECHNIQUE FOR LLR preserve collaterals on the abdominal wall in patients with
liver cirrhosis. This may require use of ultrasonography to
Patient position and setting identify collateral vessels. [32]
Under general anesthesia, the patient is positioned
depending on the location of the tumor. In general, Hepatic parenchymal transection
resection of the left hemi-liver or right anterior region of For this procedure, laparoscopic ultrasound is performed
the liver is performed with the patient in conventional using a flexible-angle ultrasound probe, to confirm the
supine position. Resection of the right posterosuperior location of the tumor in relation to the vascular anatomy
region of the liver is performed with the patient in a and identify other lesions in the liver. Although surface
left hemilateral decubitus position, especially for roughness from cirrhosis may impede ultrasound
resections requiring mobilization of the right liver from inspection, use of a water drip around the ultrasound
the retroperitoneum. In the left hemilateral position, the probe can improve penetration of the ultrasound signal
patient’s body is fixed using a negative pressure bag into the liver parenchyma.
packed with plastic beads, which is placed under the
patient, and several support arms to prevent slipping Because of the risk of CO gas embolism caused by
2
during abrupt position changes. pneumoperitoneum, [33,34] intra-abdominal pressure should
be maintained below 8-12 mmHg during the procedure. [35]
The laparoscopic tower contains the light source,
camera, and insufflators and is positioned to the right Chronic liver disease is characterized by significant
of the patient. Monopolar and bipolar generators for alterations in the intra- and extrahepatic vasculature.
electrocautery devices, a microwave tissue coagulator, Division of collaterals within the falciform ligament or
Hepatoma Research ¦ Volume 2 ¦ September 19, 2016 243