Page 36 - Read Online
P. 36
Page 6 of 12 Armengol et al. Hepatoma Res 2021;7:50 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-5079.2021.19
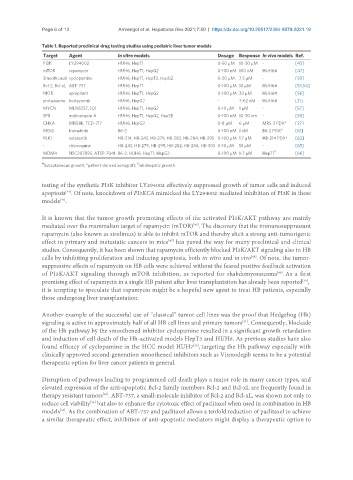
Table 1. Reported preclinical drug testing studies using pediatric liver tumor models
Target Agent In vitro models Dosage Response In vivo models Ref.
PI3K LY294002 HUH6, HepT1 0-50 µM 10-30 µM - [43]
mTOR rapamycin HUH6, HepT1, HepG2 0-100 nM 100 nM HUH6# [47]
Smoothened cyclopamine HUH6, HepT1, HepT3, HepG2 0-20 µM 7.5 µM - [50]
Bcl-2, Bcl-xL ABT-737 HUH6, HepT1 0-100 µM 10 µM HUH6# [53,54]
NK1R aprepitant HUH6, HepT1, HepG2 0-100 µM 30 µM HUH6# [56]
proteasome bortezomib HUH6, HepG2 - 7-62 nM HUH6# [31]
MYCN MLN8237, JQ1 HUH6, HepT1, HepG2 0-10 µM 1 µM - [57]
SP8 mithramycin A HUH6, HepT1, HepG2, Hep3B 0-100 nM 10-30 nm - [58]
CHKA MN58b, TCD-717 HUH6, HepG2 0-8 µM 6 µM MRS-3 PDX* [27]
MEK1 trametinib B6-2 0-100 nM 1 nM B6-2 PDX* [61]
PLK1 volasertib HB-214, HB-243, HB-279, HB-282, HB-284, HB-295 0-100 µM 1.7 µM HB-214 PDX* [63]
- chloroquine HB-243, HB-279, HB-295, HB-282, HB-284, HB-303 0-10 µM 10 µM - [65]
§
MDM4 NSC207895, ATSP-7041 B6-2, HUH6, HepT1, HepG2 0-100 µM 1-7 µM HepT1 [66]
# §
Subcutaneous growth; *patient-derived xenograft; intrahepatic growth.
testing of the synthetic PI3K inhibitor LY294002 effectively suppressed growth of tumor cells and induced
apoptosis . Of note, knockdown of PI3KCA mimicked the LY294002-mediated inhibition of PI3K in these
[44]
[44]
models .
It is known that the tumor growth promoting effects of the activated PI3K/AKT pathway are mainly
mediated over the mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) . The discovery that the immunosuppressant
[46]
rapamycin (also known as sirolimus) is able to inhibit mTOR and thereby elicit a strong anti-tumorigenic
effect in primary and metastatic cancers in mice has paved the way for many preclinical and clinical
[47]
studies. Consequently, it has been shown that rapamycin efficiently blocked PI3K/AKT signaling also in HB
cells by inhibiting proliferation and inducing apoptosis, both in vitro and in vivo . Of note, the tumor-
[48]
suppressive effects of rapamycin on HB cells were achieved without the feared positive feedback activation
of PI3K/AKT signaling through mTOR inhibition, as reported for rhabdomyosarcoma . As a first
[49]
promising effect of rapamycin in a single HB patient after liver transplantation has already been reported ,
[50]
it is tempting to speculate that rapamycin might be a hopeful new agent to treat HB patients, especially
those undergoing liver transplantation.
Another example of the successful use of “classical” tumor cell lines was the proof that Hedgehog (Hh)
[51]
signaling is active in approximately half of all HB cell lines and primary tumors . Consequently, blockade
of the Hh pathway by the smoothened inhibitor cyclopamine resulted in a significant growth retardation
and induction of cell death of the Hh-activated models HepT3 and HUH6. As previous studies have also
[52]
found efficacy of cyclopamine in the HCC model HUH7 , targeting the Hh pathway especially with
clinically approved second-generation smoothened inhibitors such as Vismodegib seems to be a potential
therapeutic option for liver cancer patients in general.
Disruption of pathways leading to programmed cell death plays a major role in many cancer types, and
elevated expression of the anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 family members Bcl-2 and Bcl-xL are frequently found in
therapy resistant tumors . ABT-737, a small-molecule inhibitor of Bcl-2 and Bcl-xL, was shown not only to
[53]
reduce cell viability but also to enhance the cytotoxic effect of paclitaxel when used in combination in HB
[54]
models . As the combination of ABT-737 and paclitaxel allows a tenfold reduction of paclitaxel to achieve
[55]
a similar therapeutic effect, inhibition of anti-apoptotic mediators might display a therapeutic option to