Page 50 - Read Online
P. 50
Yang et al. Hepatoma Res 2020;6:37 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-5079.2020.09 Page 7 of 13
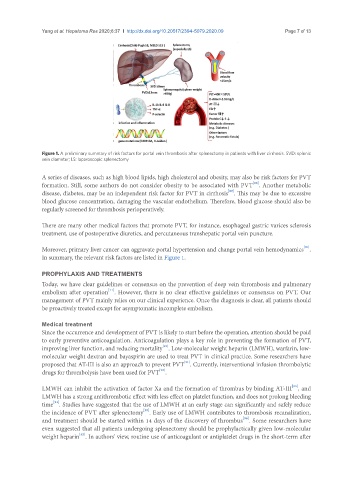
Figure 1. A preliminary summary of risk factors for portal vein thrombosis after splenectomy in patients with liver cirrhosis. SVD: splenic
vein diameter; LS: laparoscopic splenectomy
A series of diseases, such as high blood lipids, high cholesterol and obesity, may also be risk factors for PVT
[88]
formation. Still, some authors do not consider obesity to be associated with PVT . Another metabolic
[89]
disease, diabetes, may be an independent risk factor for PVT in cirrhosis . This may be due to excessive
blood glucose concentration, damaging the vascular endothelium. Therefore, blood glucose should also be
regularly screened for thrombosis perioperatively.
There are many other medical factors that promote PVT, for instance, esophageal gastric varices sclerosis
treatment, use of postoperative diuretics, and percutaneous transhepatic portal vein puncture.
[90]
Moreover, primary liver cancer can aggravate portal hypertension and change portal vein hemodynamics .
In summary, the relevant risk factors are listed in Figure 1.
PROPHYLAXIS AND TREATMENTS
Today, we have clear guidelines or consensus on the prevention of deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary
[11]
embolism after operation . However, there is no clear effective guidelines or consensus on PVT. Our
management of PVT mainly relies on our clinical experience. Once the diagnosis is clear, all patients should
be proactively treated except for asymptomatic incomplete embolism.
Medical treatment
Since the occurrence and development of PVT is likely to start before the operation, attention should be paid
to early preventive anticoagulation. Anticoagulation plays a key role in preventing the formation of PVT,
[91]
improving liver function, and reducing mortality . Low-molecular weight heparin (LMWH), warfarin, low-
molecular weight dextran and bayaspirin are used to treat PVT in clinical practice. Some researchers have
[51]
proposed that AT-III is also an approach to prevent PVT . Currently, interventional infusion thrombolytic
[92]
drugs for thrombolysis have been used for PVT .
[93]
LMWH can inhibit the activation of factor Xa and the formation of thrombus by binding AT-III , and
LMWH has a strong antithrombotic effect with less effect on platelet function, and does not prolong bleeding
[94]
time . Studies have suggested that the use of LMWH at an early stage can significantly and safely reduce
[95]
the incidence of PVT after splenectomy . Early use of LMWH contributes to thrombosis recanalization,
[96]
and treatment should be started within 14 days of the discovery of thrombus . Some researchers have
even suggested that all patients undergoing splenectomy should be prophylactically given low-molecular
[42]
weight heparin . In authors’ view, routine use of anticoagulant or antiplatelet drugs in the short-term after