Page 34 - Read Online
P. 34
Page 2 of 14 Moriguchi et al. Hepatoma Res 2019;5:43 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-5079.2019.20
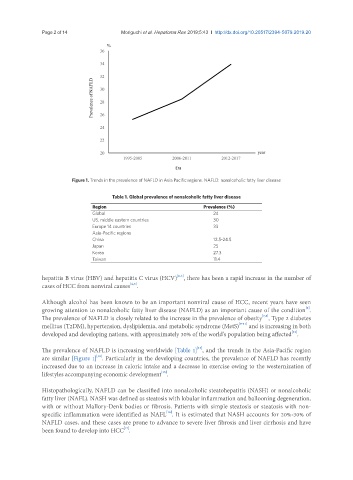
Figure 1. Trends in the prevalence of NAFLD in Asia Pacific regions. NAFLD: nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
Table 1. Global prevalence of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
Region Prevalence (%)
Global 24
US, middle eastern countries 30
Europe 14 countries 33
Asia-Pacific regions
China 12.5-24.5
Japan 25
Korea 27.3
Taiwan 11.4
[2,3]
hepatitis B virus (HBV) and hepatitis C virus (HCV) , there has been a rapid increase in the number of
[4,5]
cases of HCC from nonviral causes .
Although alcohol has been known to be an important nonviral cause of HCC, recent years have seen
growing attention to nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) as an important cause of the condition .
[6]
[7,8]
The prevalence of NAFLD is closely related to the increase in the prevalence of obesity , Type 2 diabetes
mellitus (T2DM), hypertension, dyslipidemia, and metabolic syndrome (MetS) [9-11] and is increasing in both
[12]
developed and developing nations, with approximately 30% of the world’s population being affected .
[13]
The prevalence of NAFLD is increasing worldwide [Table 1] , and the trends in the Asia-Pacific region
[14]
are similar [Figure 1] . Particularly in the developing countries, the prevalence of NAFLD has recently
increased due to an increase in caloric intake and a decrease in exercise owing to the westernization of
[15]
lifestyles accompanying economic development .
Histopathologically, NAFLD can be classified into nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) or nonalcoholic
fatty liver (NAFL). NASH was defined as steatosis with lobular inflammation and ballooning degeneration,
with or without Mallory-Denk bodies or fibrosis. Patients with simple steatosis or steatosis with non-
[16]
specific inflammation were identified as NAFL . It is estimated that NASH accounts for 20%-30% of
NAFLD cases, and these cases are prone to advance to severe liver fibrosis and liver cirrhosis and have
[17]
been found to develop into HCC .