Page 219 - Read Online
P. 219
Matsushita et al. Hepatoma Res 2018;4:61 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-5079.2018.81 Page 13 of 17
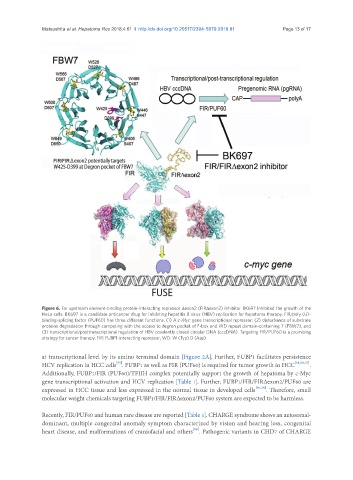
Figure 6. Far upstream element-binding protein-interacting repressor Δexon2 (FIRΔexon2) inhibitor BK697 inhibited the growth of the
HeLa cells. BK697 is a candidate anticancer drug for inhibiting hepatitis B virus (HBV) replication for hepatoma therapy. FIR/poly (U)-
binding-splicing factor (PUF60) has three different functions. (1) A c-Myc gene transcriptional repressor; (2) disturbance of substrate
proteins degradation through competing with the access to degron pocket of F-box and WD repeat domain-containing 7 (FBW7); and
(3) transcriptional/posttranscriptional regulation of HBV covalently closed circular DNA (cccDNA). Targeting FIR/PUF60 is a promising
strategy for cancer therapy. FIR: FUBP1-interacting repressor; WD: W (Typ) D (Asp)
at transcriptional level by its amino terminal domain [Figure 2A]. Further, FUBP1 facilitates persistence
[55]
HCV replication in HCC cells . FUBP1 as well as FIR (PUF60) is required for tumor growth in HCC [38,56,57] .
Additionally, FUBP1/FIR (PUF60)/TFIIH complex potentially support the growth of hepatoma by c-Myc
gene transcriptional activation and HCV replication [Table 1]. Further, FUBP1/FIR/FIRΔexon2/PUF60 are
expressed in HCC tissue and less expressed in the normal tissue in developed cells [18,38] . Therefore, small
molecular weight chemicals targeting FUBP1/FIR/FIRΔexon2/PUF60 system are expected to be harmless.
Recently, FIR/PUF60 and human rare disease are reported [Table 1]. CHARGE syndrome shows an autosomal-
dominant, multiple congenital anomaly symptom characterized by vision and hearing loss, congenital
[58]
heart disease, and malformations of craniofacial and others . Pathogenic variants in CHD7 of CHARGE