Page 99 - Read Online
P. 99
Page 4 of 15 Correnti et al. Hepatoma Res 2018;4:69 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-5079.2018.96
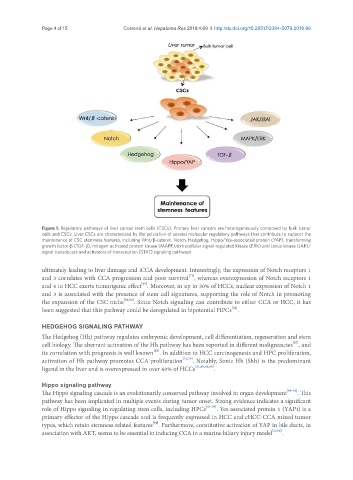
Figure 1. Regulatory pathways of liver cancer stem cells (CSCs). Primary liver cancers are heterogeneously composed by bulk tumor
cells and CSCs. Liver CSCs are characterized by the activation of several molecular regulatory pathways that contribute to support the
maintenance of CSC stemness features, including Wnt/β-catenin, Notch, Hedgehog, Hippo/Yes-associated protein (YAP), transforming
growth factor-β (TGF-β), mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK)/extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) and Janus kinase (JAK)/
signal transducers and activators of transcription (STAT) signaling pathways
ultimately leading to liver damage and iCCA development. Interestingly, the expression of Notch receptors 1
[71]
and 3 correlates with CCA progression and poor survival , whereas overexpression of Notch receptors 1
[85]
and 4 in HCC exerts tumorigenic effect . Moreover, in up to 30% of HCCs, nuclear expression of Notch 1
and 3 is associated with the presence of stem cell signatures, supporting the role of Notch in promoting
the expansion of the CSC niche [81,86] . Since Notch signaling can contribute to either CCA or HCC, it has
[82]
been suggested that this pathway could be deregulated in bipotential HPCs .
HEDGEHOG SIGNALING PATHWAY
The Hedgehog (Hh) pathway regulates embryonic development, cell differentiation, regeneration and stem
[87]
cell biology. The aberrant activation of the Hh pathway has been reported in different malignancies , and
[88]
its correlation with prognosis is well known . In addition to HCC carcinogenesis and HPC proliferation,
activation of Hh pathway promotes CCA proliferation [71,79] . Notably, Sonic Hh (Shh) is the predominant
ligand in the liver and is overexpressed in over 60% of HCCs [31,69,81,89] .
Hippo signaling pathway
The Hippo signaling cascade is an evolutionarily conserved pathway involved in organ development [90-92] . This
pathway has been implicated in multiple events during tumor onset. Strong evidence indicates a significant
role of Hippo signaling in regulating stem cells, including HPCs [93-95] . Yes-associated protein 1 (YAP1) is a
primary effector of the Hippo cascade and is frequently expressed in HCC and cHCC-CCA mixed tumor
[94]
types, which retain stemness-related features . Furthermore, constitutive activation of YAP in bile ducts, in
association with AKT, seems to be essential in inducing CCA in a murine biliary injury model [31,96] .