Page 179 - Read Online
P. 179
Ding et al. Hepatoma Res 2018;4:12 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-5079.2018.07 Page 5 of 8
d
0.5
b TNF-α
e
IL-1β
0.4
c
AFP
a
0.3
0.2
0.1
0.0
A B C D E F
Groups
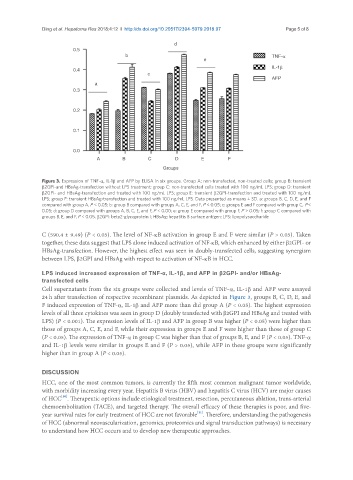
Figure 3. Expression of TNF-α, IL-1β and AFP by ELISA in six groups. Group A: non-transfected, non-treated cells; group B: transient
β2GPI-and HBsAg-transfection without LPS treatment; group C: non-transfected cells treated with 100 ng/mL LPS; group D: transient
β2GPI- and HBsAg-transfection and treated with 100 ng/mL LPS; group E: transient β2GPI-transfection and treated with 100 ng/mL
LPS; group F: transient HBsAg-transfection and treated with 100 ng/mL LPS. Data presented as means ± SD. a: groups B, C, D, E, and F
compared with group A, P < 0.05; b: group B compared with groups A, C, E, and F, P < 0.05; c: groups E and F compared with group C, P <
0.05; d: group D compared with groups A, B, C, E, and F, P < 0.00; e: group E compared with group F, P > 0.05; f: group C compared with
groups B, E, and F, P < 0.05. β2GPI: beta2-glycoprotein I; HBsAg: hepatitis B surface antigen; LPS: lipopolysaccharide
C (590.4 ± 9.49) (P < 0.05). The level of NF-κB activation in group E and F were similar (P > 0.05). Taken
together, these data suggest that LPS alone induced activation of NF-κB, which enhanced by either β2GPI- or
HBsAg-transfection. However, the highest effect was seen in doubly-transfected cells, suggesting synergism
between LPS, β2GPI and HBsAg with respect to activation of NF-κB in HCC.
LPS induced increased expression of TNF-α, IL-1β, and AFP in β2GPI- and/or HBsAg-
transfected cells
Cell supernatants from the six groups were collected and levels of TNF-α, IL-1β and AFP were assayed
24 h after transfection of respective recombinant plasmids. As depicted in Figure 3, groups B, C, D, E, and
F induced expression of TNF-α, IL-1β and AFP more than did group A (P < 0.05). The highest expression
levels of all three cytokines was seen in group D (doubly transfected with β2GPI and HBsAg and treated with
LPS) (P < 0.001). The expression levels of IL-1β and AFP in group B was higher (P < 0.05) were higher than
those of groups A, C, E, and F, while their expression in groups E and F were higher than those of group C
(P < 0.05). The expression of TNF-α in group C was higher than that of groups B, E, and F (P < 0.05). TNF-α
and IL-1β levels were similar in groups E and F (P > 0.05), while AFP in these groups were significantly
higher than in group A (P < 0.05).
DISCUSSION
HCC, one of the most common tumors, is currently the fifth most common malignant tumor worldwide,
with morbidity increasing every year. Hepatitis B virus (HBV) and hepatitis C virus (HCV) are major causes
[10]
of HCC . Therapeutic options include etiological treatment, resection, percutaneous ablation, trans-arterial
chemoembolization (TACE), and targeted therapy. The overall efficacy of these therapies is poor, and five-
[11]
year survival rates for early treatment of HCC are not favorable . Therefore, understanding the pathogenesis
of HCC (abnormal neovascularization, genomics, proteomics and signal transduction pathways) is necessary
to understand how HCC occurs and to develop new therapeutic approaches.