Page 195 - Read Online
P. 195
Page 4 of 13 Pan et al. Hepatoma Res 2024;10:3 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-5079.2023.44
Table 1. Top actionable mutation targets and corresponding drugs in ICC
Mutation gene Mutation rate Reference Targeted drugs FDA approved
FGFR2 11% to 45% [17,20,26] Pemigatinib yes
Infigratinib yes
Futibatinib yes
Derazantinib no
IDH1 15%-20% [37] Ivosidenib yes
BRAF 1%-5% [27] Dabrafenib yes
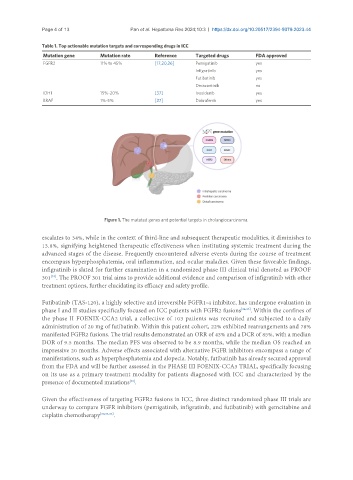
Figure 1. The mutated genes and potential targets in cholangiocarcinoma.
escalates to 34%, while in the context of third-line and subsequent therapeutic modalities, it diminishes to
13.8%, signifying heightened therapeutic effectiveness when instituting systemic treatment during the
advanced stages of the disease. Frequently encountered adverse events during the course of treatment
encompass hyperphosphatemia, oral inflammation, and ocular maladies. Given these favorable findings,
infigratinib is slated for further examination in a randomized phase III clinical trial denoted as PROOF
301 . The PROOF 301 trial aims to provide additional evidence and comparison of infigratinib with other
[33]
treatment options, further elucidating its efficacy and safety profile.
Futibatinib (TAS-120), a highly selective and irreversible FGFR1-4 inhibitor, has undergone evaluation in
phase I and II studies specifically focused on ICC patients with FGFR2 fusions [34,35] . Within the confines of
the phase II FOENIX-CCA2 trial, a collective of 103 patients was recruited and subjected to a daily
administration of 20 mg of futibatinib. Within this patient cohort, 22% exhibited rearrangements and 78%
manifested FGFR2 fusions. The trial results demonstrated an ORR of 43% and a DCR of 85%, with a median
DOR of 9.5 months. The median PFS was observed to be 8.9 months, while the median OS reached an
impressive 20 months. Adverse effects associated with alternative FGFR inhibitors encompass a range of
manifestations, such as hyperphosphatemia and alopecia. Notably, futibatinib has already secured approval
from the FDA and will be further assessed in the PHASE III FOENIX-CCA3 TRIAL, specifically focusing
on its use as a primary treatment modality for patients diagnosed with ICC and characterized by the
[36]
presence of documented mutations .
Given the effectiveness of targeting FGFR2 fusions in ICC, three distinct randomized phase III trials are
underway to compare FGFR inhibitors (pemigatinib, infigratinib, and futibatinib) with gemcitabine and
cisplatin chemotherapy [30,33,36] .