Page 127 - Read Online
P. 127
Page 4 of 12 An et al. Hepatoma Res 2023;9:43 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-5079.2023.60
Table 1. Prior studies investigating TARE in treatment of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma
Author Study type Sample size Technique Outcomes
Rafi et al. (2012) [26] Retrospective n = 19 TARE with y90 resin microspheres Median OS = 11.5 months
[31]
Bargellini et al. (2020) Retrospective n = 81 TARE Median OS = 14.5 months
[28]
Saxena et al. (2010) Retrospective n = 25 TARE with y90 resin microspheres Median OS = 9.3 months
[29]
Hoffman et al. (2012) Retrospective n = 33 TARE with y90 resin microspheres Median PFS = 9.8 months
Median OS = 22 months
Buettner et al. (2020) [30] Retrospective n = 114 TARE Median OS = 29 months
[33]
Gangi et al. (2018) Retrospective n = 85 TARE with y90 glass microspheres Median OS = 12 months
Mouli et al. (2013) [34] Retrospective n = 46 TARE Median OS = 14.6 months (solitary disease)
TARE: trans-arterial radioembolization.
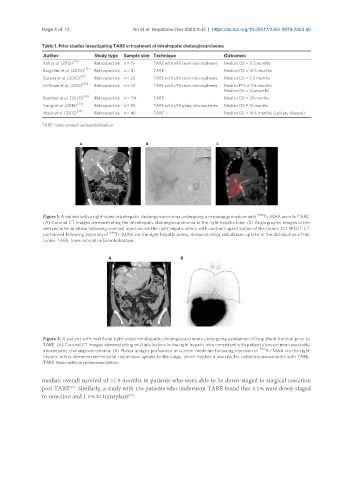
Figure 1. A patient with a right-sided intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma undergoing a mapping procedure with 99m Tc-MAA prior to TARE.
(A) Coronal CT images demonstrating the intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma in the right hepatic lobe; (B) Angiographic images in the
delayed arterial phase following contrast injection via the right hepatic artery with contrast opacification of the tumor; (C) SPECT-CT
performed following injection of 99m Tc-MAA via the right hepatic artery, demonstrating radiotracer uptake in the distribution of the
tumor. TARE: trans-arterial radioembolization.
Figure 2. A patient with multifocal right-sided intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma undergoing evaluation of lung shunt fraction prior to
TARE. (A) Coronal CT images demonstrating multiple lesions in the right hepatic lobe consistent with patient’s known non-resectable
intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma; (B) Planar images performed in nuclear medicine following injection of 99m Tc-MAA via the right
hepatic artery demonstrate minimal radiotracer uptake to the lungs, which implies a low risk for radiation pneumonitis with TARE.
TARE: trans-arterial radioembolization.
median overall survival of 51.9 months in patients who were able to be down-staged to surgical resection
post TARE . Similarly, a study with 136 patients who underwent TARE found that 8.1% were down-staged
[27]
[35]
to resection and 1.5% to transplant .