Page 8 - Read Online
P. 8
Page 4 of 14 Ma et al. Complex Eng Syst 2023;3:10 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/ces.2023.14
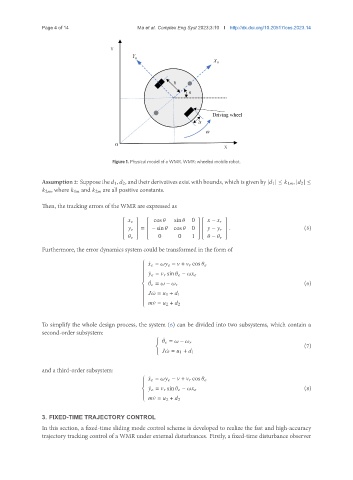
Figure 1. Physical model of a WMR. WMR: wheeled mobile robot.
Assumption2: Suppose the 1, 2, andtheir derivatives exist with bounds, which is given by | 1 | ≤ 1 , | 2 | ≤
2 , where 1 and 2 are all positive constants.
Then, the tracking errors of the WMR are expressed as
cos sin
0 −
= − sin cos 0 . (5)
−
0 0 1
−
Furthermore, the error dynamics system could be transformed in the form of
¤ = − + cos
¤ = sin −
¤ (6)
= −
¤ = 1 + 1
¤ = 2 + 2
To simplify the whole design process, the system (6) can be divided into two subsystems, which contain a
second-order subsystem:
(
¤
= −
(7)
¤ = 1 + 1
and a third-order subsystem:
¤ = − + cos
¤ = sin − (8)
¤ = 2 + 2
3. FIXED-TIME TRAJECTORY CONTROL
In this section, a fixed-time sliding mode control scheme is developed to realize the fast and high-accuracy
trajectory tracking control of a WMR under external disturbances. Firstly, a fixed-time disturbance observer