Page 107 - Read Online
P. 107
Abaji et al. Cancer Drug Resist 2019;2:242-55 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/cdr.2018.24 Page 245
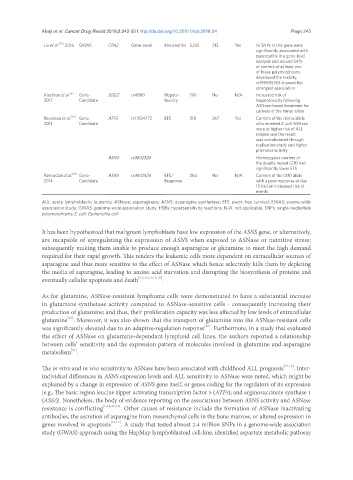
Liu et al. [35] 2016 GWAS CPA2 Gene-Level Pancreatitis 5,185 213 Yes 16 SNPs in this gene were
significantly associated with
pancreatitis in a gene-level
analysis and around 54%
of carriers of at least one
of these polymorphisms
developed the toxicity.
rs199695765 showed the
strongest association
Alachkar et al. Gene- SOD2 rs4880 Hepato- 190 No N/A Increased risk of
[6]
2017 Candidate toxicity hepatotoxicity following
ASNase-based treatment for
carriers of the minor allele
Rousseau et al. [18] Gene- ATF5 rs11554772 EFS 318 267 Yes Carriers of the minor allele
2011 Candidate who received E. coli ASNase
were at higher risk of ALL
relapse and the result
was corroborated through
replication study and higher
promoter activity
ASNS rs3832526 Homozygous carriers of
the double repeat (2R) had
significantly lower EFS
Pastorczak et al. [54] Gene- ASNS rs3832526 EFS/ 264 No N/A Carriers of the (3R) allele
2014 Candidate Response with a poor response at day
15 had an increased risk of
events
ALL: acute lymphoblastic leukemia; ASNase: asparaginase; ASNS: asparagine synthetase; EFS: event-free survival; EWAS: exome-wide
association study; GWAS: genome-wide association study; HSRs: hypersensitivity reactions; N/A: not applicable; SNPs: single-nucleotide
polymorphisms; E. coli: Escherichia coli
It has been hypothesized that malignant lymphoblasts have low expression of the ASNS gene, or alternatively,
are incapable of upregulating the expression of ASNS when exposed to ASNase or nutritive stress;
subsequently making them unable to produce enough asparagine or glutamine to meet the high demand
required for their rapid growth. This renders the leukemic cells more dependent on extracellular sources of
asparagine and thus more sensitive to the effect of ASNase which hence selectively kills them by depleting
the media of asparagine, leading to amino acid starvation and disrupting the biosynthesis of proteins and
eventually cellular apoptosis and death [2,7,10,14,18,19] .
As for glutamine, ASNase-resistant lymphoma cells were demonstrated to have a substantial increase
in glutamine synthetase activity compared to ASNase-sensitive cells - consequently increasing their
production of glutamine; and thus, their proliferation capacity was less affected by low levels of extracellular
[20]
glutamine . Moreover, it was also shown that the transport of glutamine into the ASNase-resistant cells
[20]
was significantly elevated due to an adaptive-regulation response . Furthermore, in a study that evaluated
the effect of ASNase on glutamine-dependant lymphoid cell lines, the authors reported a relationship
between cells’ sensitivity and the expression pattern of molecules involved in glutamine and asparagine
[21]
metabolism .
The in vitro and in vivo sensitivity to ASNase have been associated with childhood ALL prognosis [14,19] . Inter-
individual differences in ASNS expression levels and ALL sensitivity to ASNase were noted, which might be
explained by a change in expression of ASNS gene itself, or genes coding for the regulators of its expression
[e.g., The basic region leucine zipper activating transcription factor 5 (ATF5); and arginosuccinate synthase 1
(ASS1)]. Nonetheless, the body of evidence reporting on the associations between ASNS activity and ASNase
resistance is conflicting [5,14,18,19] . Other causes of resistance include the formation of ASNase inactivating
antibodies, the secretion of asparagine from mesenchymal cells in the bone marrow, or altered expression in
genes involved in apoptosis [14,19] . A study that tested almost 2.4 million SNPs in a genome-wide association
study (GWAS) approach using the HapMap lymphoblastoid cell-line, identified aspartate metabolic pathway