Page 96 - Read Online
P. 96
Zhang et al. Cancer Drug Resist 2024;7:34 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/cdr.2024.59 Page 7 of 20
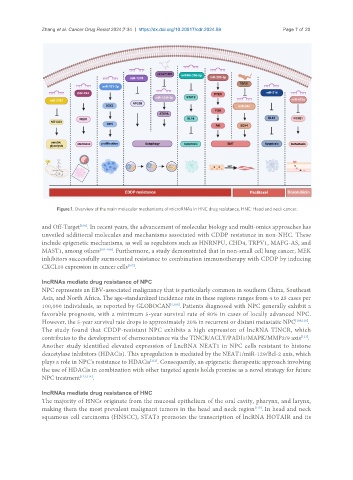
Figure 1. Overview of the main molecular mechanisms of microRNAs in HNC drug resistance. HNC: Head and neck cancer.
and Off-Target . In recent years, the advancement of molecular biology and multi-omics approaches has
[100]
unveiled additional molecules and mechanisms associated with CDDP resistance in non-NHC. These
include epigenetic mechanisms, as well as regulators such as HNRNPU, CHD4, TRPV1, MAFG-AS, and
MAST1, among others [101-106] . Furthermore, a study demonstrated that in non-small cell lung cancer, MEK
inhibitors successfully surmounted resistance to combination immunotherapy with CDDP by inducing
[107]
CXCL10 expression in cancer cells .
lncRNAs mediate drug resistance of NPC
NPC represents an EBV-associated malignancy that is particularly common in southern China, Southeast
Asia, and North Africa. The age-standardized incidence rate in these regions ranges from 4 to 25 cases per
100,000 individuals, as reported by GLOBOCAN [5,108] . Patients diagnosed with NPC generally exhibit a
favorable prognosis, with a minimum 5-year survival rate of 80% in cases of locally advanced NPC.
However, the 5-year survival rate drops to approximately 20% in recurrent or distant metastatic NPC [109,110] .
The study found that CDDP-resistant NPC exhibits a high expression of lncRNA TINCR, which
contributes to the development of chemoresistance via the TINCR/ACLY/PADI1/MAPK/MMP2/9 axis .
[111]
Another study identified elevated expression of LncRNA NEAT1 in NPC cells resistant to histone
deacetylase inhibitors (HDACis). This upregulation is mediated by the NEAT1/miR-129/Bcl-2 axis, which
[112]
plays a role in NPC's resistance to HDACis . Consequently, an epigenetic therapeutic approach involving
the use of HDACis in combination with other targeted agents holds promise as a novel strategy for future
NPC treatment [113,114] .
lncRNAs mediate drug resistance of HNC
The majority of HNCs originate from the mucosal epithelium of the oral cavity, pharynx, and larynx,
[115]
making them the most prevalent malignant tumors in the head and neck region . In head and neck
squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC), STAT3 promotes the transcription of lncRNA HOTAIR and its