Page 68 - Read Online
P. 68
Genovese et al. Cancer Drug Resist 2018;1:164-80 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/cdr.2018.10 Page 167
+
2+
2+
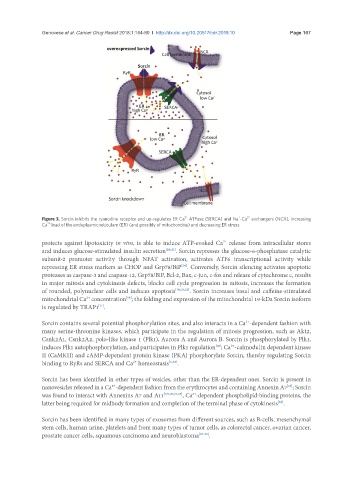
Figure 3. Sorcin inhibits the ryanodine receptor and up-regulates ER Ca ATPase (SERCA) and Na -Ca exchangers (NCX), increasing
2+
Ca load of the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) (and possibly of mitochondria) and decreasing ER stress
protects against lipotoxicity in vivo, is able to induce ATP-evoked Ca release from intracellular stores
2+
and induces glucose-stimulated insulin secretion [20,21] . Sorcin represses the glucose-6-phosphatase catalytic
subunit-2 promoter activity through NFAT activation, activates ATF6 transcriptional activity while
repressing ER stress markers as CHOP and Grp78/BiP . Conversely, Sorcin silencing activates apoptotic
[20]
proteases as caspase-3 and caspase-12, Grp78/BiP, Bcl-2, Bax, c-jun, c-fos and release of cytochrome c, results
in major mitosis and cytokinesis defects, blocks cell cycle progression in mitosis, increases the formation
of rounded, polynuclear cells and induces apoptosis [10,18,22] . Sorcin increases basal and caffeine-stimulated
mitochondrial Ca concentration ; the folding and expression of the mitochondrial 19-kDa Sorcin isoform
2+
[18]
is regulated by TRAP1 .
[11]
Sorcin contains several potential phosphorylation sites, and also interacts in a Ca -dependent fashion with
2+
many serine-threonine kinases, which participate in the regulation of mitosis progression, such as Akt2,
Csnk2A1, Csnk2A2, polo-like kinase 1 (Plk1), Aurora A and Aurora B. Sorcin is phosphorylated by Plk1,
induces Plk1 autophosphorylation, and participates in Plk1 regulation ; Ca -calmodulin dependent kinase
2+
[10]
II (CaMKII) and cAMP-dependent protein kinase (PKA) phosphorylate Sorcin, thereby regulating Sorcin
2+
binding to RyRs and SERCA and Ca homeostasis [6,23] .
Sorcin has been identified in other types of vesicles, other than the ER-dependent ones. Sorcin is present in
nanovesicles released in a Ca -dependent fashion from the erythrocytes and containing Annexin A7 ; Sorcin
2+
[24]
was found to interact with Annexins A7 and A11 [7,8,10,15,25] , Ca -dependent phospholipid-binding proteins, the
2+
latter being required for midbody formation and completion of the terminal phase of cytokinesis .
[26]
Sorcin has been identified in many types of exosomes from different sources, such as B-cells, mesenchymal
stem cells, human urine, platelets and from many types of tumor cells, as colorectal cancer, ovarian cancer,
prostate cancer cells, squamous carcinoma and neuroblastoma [27-35] .