Page 78 - Read Online
P. 78
Sharma et al. Cancer Drug Resist 2023;6:688-708 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/cdr.2023.82 Page 694
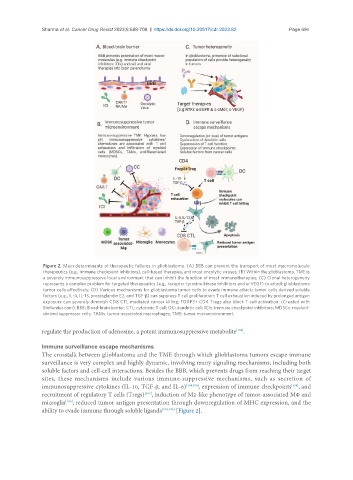
Figure 2. Main determinants of therapeutic failures in glioblastoma. (A) BBB can prevent the transport of most macromolecule
therapeutics (e.g., immune checkpoint inhibitors), cell-based therapies, and most oncolytic viruses; (B) Within the glioblastoma, TME is
a severely immunosuppressive local environment that can inhibit the function of most immunotherapies; (C) Clonal heterogeneity
represents a complex problem for targeted therapeutics (e.g., receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors and α-VEGF) to attack glioblastoma
tumor cells effectively; (D) Various mechanisms for glioblastoma tumor cells to evade immune attack: tumor cells derived soluble
factors (e.g., IL-4, IL-13, prostaglandin E2, and TGF-β) can suppress T cell proliferation; T cell exhaustion induced by prolonged antigen
exposure can severely diminish CD8 CTL mediated cancer killing; FOXP3+ CD4 Tregs also block T cell activation. (Created with
BioRender.com). BBB: Blood-brain barrier; CTL: cytotoxic T cell; DC: dendritic cell; ICIs: immune checkpoint inhibitors; MDSCs: myeloid-
derived suppressor cells; TAMs: tumor-associated macrophages; TME: tumor microenvironment.
regulate the production of adenosine, a potent immunosuppressive metabolite .
[102]
Immune surveillance escape mechanisms
The crosstalk between glioblastoma and the TME through which glioblastoma tumors escape immune
surveillance is very complex and highly dynamic, involving many signaling mechanisms, including both
soluble factors and cell-cell interactions. Besides the BBB, which prevents drugs from reaching their target
sites, these mechanisms include various immune-suppressive mechanisms, such as secretion of
immunosuppressive cytokines (IL-10, TGF-β, and IL-6) [104,105] , expression of immune checkpoints , and
[106]
recruitment of regulatory T cells (Tregs) , induction of M2-like phenotype of tumor-associated MΦ and
[107]
microglia , reduced tumor antigen presentation through downregulation of MHC expression, and the
[106]
ability to evade immune through soluble ligands [108,109] [Figure 2].