Page 71 - Read Online
P. 71
Page 353 Hogue et al. Art Int Surg. 2025;5:350-60 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/ais.2025.19
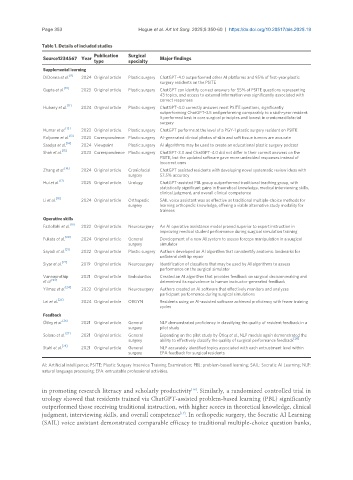
Table 1. Details of included studies
Publication Surgical
Source1234567 Year Major findings
type specialty
Supplemental learning
DiDonna et al. [9] 2024 Original article Plastic surgery ChatGPT-4.0 outperformed other AI platforms and 95% of first-year plastic
surgery residents on the PSITE
Gupta et al. [10] 2023 Original article Plastic surgery ChatGPT can identify correct answers for 55% of PSITE questions representing
43 topics, and access to external information was significantly associated with
correct responses
[11]
Hubany et al. 2024 Original article Plastic surgery ChatGPT-4.0 correctly answers most PSITE questions, significantly
outperforming ChatGPT-3.5 and performing comparably to a sixth-year resident.
It performed best in core surgical principles and lowest in craniomaxillofacial
surgery
Humar et al. [12] 2023 Original article Plastic surgery ChatGPT performs at the level of a PGY-1 plastic surgery resident on PSITE
[13]
Koljonen et al. 2023 Correspondence Plastic surgery AI-generated clinical photos of skin and soft tissue tumors are accurate
Saadya et al. [14] 2024 Viewpoint Plastic surgery AI algorithms may be used to create an educational plastic surgery podcast
[15]
Shah et al. 2023 Correspondence Plastic surgery ChatGPT-3.0 and ChatGPT-4.0 did not differ in their correct answers on the
PSITE, but the updated software gave more undecided responses instead of
incorrect ones
Zhang et al. [16] 2024 Original article Craniofacial ChatGPT assisted residents with developing novel systematic review ideas with
surgery 57.5% accuracy
Hui et al. [17] 2025 Original article Urology ChatGPT-assisted PBL group outperformed traditional teaching group, with
statistically significant gains in theoretical knowledge, medical interviewing skills,
clinical judgment, and overall clinical competence
[18]
Li et al. 2024 Original article Orthopedic SAIL voice assistant was as effective as traditional multiple-choice methods for
surgery learning orthopedic knowledge, offering a viable alternative study modality for
trainees
Operative skills
[19]
Fazlollahi et al. 2022 Original article Neurosurgery An AI operative assistance model proved superior to expert instruction in
improving medical student performance during surgical simulation training
Fukata et al. [20] 2024 Original article General Development of a new AI system to assess forceps manipulation in a surgical
surgery simulator
Sayadi et al. [21] 2022 Original article Plastic surgery Authors developed an AI algorithm that can identify anatomic landmarks for
unilateral cleft lip repair
Siyar et al. [22] 2019 Original article Neurosurgery Identification of classifiers that may be used by AI algorithms to assess
performance on the surgical simulator
Vannaprathip 2021 Original article Endodontics Created an AI algorithm that provides feedback on surgical decision making and
et al. [23] determined its equivalence to human instructor-generated feedback
[24]
Yilmaz et al. 2022 Original article Neurosurgery Authors created an AI software that effectively monitors and analyzes
participant performance during surgical simulations
[25]
Lei et al. 2024 Original article OBGYN Residents using an AI-assisted software achieved proficiency with fewer training
cycles
Feedback
[26]
Ötleş et al. 2021 Original article General NLP demonstrated proficiency in classifying the quality of resident feedback in a
surgery pilot study
Solano et al. [27] 2021 Original article General Expanding on the pilot study by Ötleş et al., NLP models again demonstrated the
[26]
surgery ability to effectively classify the quality of surgical performance feedback
Stahl et al. [28] 2021 Original article General NLP accurately identified topics associated with each entrustment level within
surgery EPA feedback for surgical residents
AI: Artificial intelligence; PSITE: Plastic Surgery Inservice Training Examination; PBL: problem-based learning; SAIL: Socratic AI Learning; NLP:
natural language processing; EPA: entrustable professional activities.
in promoting research literacy and scholarly productivity . Similarly, a randomized controlled trial in
[16]
urology showed that residents trained via ChatGPT-assisted problem-based learning (PBL) significantly
outperformed those receiving traditional instruction, with higher scores in theoretical knowledge, clinical
judgment, interviewing skills, and overall competence . In orthopedic surgery, the Socratic AI Learning
[17]
(SAIL) voice assistant demonstrated comparable efficacy to traditional multiple-choice question banks,